Choosing a pipe for heating: what are the best materials?
The standard heating system in a city apartment provides for a wiring of metal pipes. On the modern market, you can find a much wider variety of materials that can be used for internal autonomous or district heating. In order to understand this assortment and make the right choice, it is worth knowing which pipes for heating are best suited in different situations.
The content of the article [Hide]
Heating pipes: which ones are better?
Among the main parameters that determine which pipes are better to use for heating, it is worth noting:
Both the temperature of the coolant and its working pressure matter for the selection. A certain influence is also exerted by the maintainability of the material, its service life and the mass of a running meter. And even the requirements for the installation of the pipeline. And one of the most important factors that are guided by when conducting a heating system in a large building (especially a two- or three-story one) is the cost of a pipe.
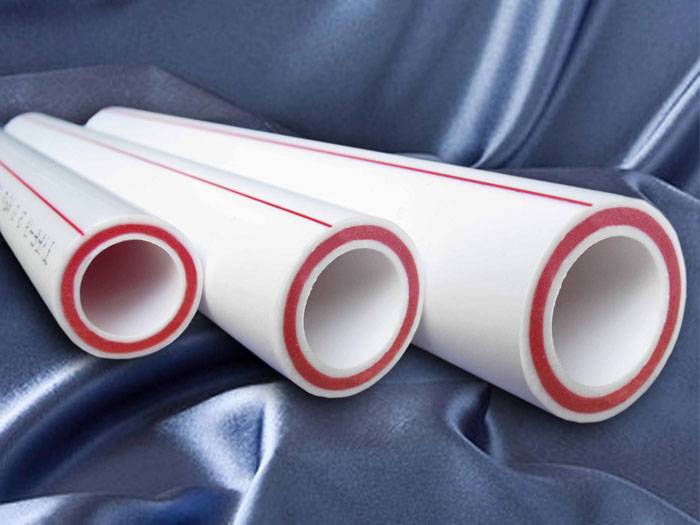
Technical characteristics of polypropylene pipes for heating
A heating pipe made of polypropylene is one of the most cost effective options. So, the cost of products suitable for underfloor heating systems, is approximately 25-30 rubles. for 1 p.m., and for polypropylene pipes withstanding a higher temperature for heating, the price per meter starts from 35-40 rubles.
In addition, the material has quite suitable parameters for both heating systems of private housesand for apartment centralized heating systems. Although not every polypropylene pipe able to withstand the high temperature of the working environment. And for this, only special reinforced polypropylene is chosen. The use of common material can deform the pipes and create an emergency.
Table 1. Polypropylene pipes for heating: technical characteristics
There are three types of polypropylene pipelines that are most often used to create indoor or indoor heating systems:
All these pipes are assembled by welding using special soldering irons. At the same time, the most convenient option for installation is with fiberglass reinforcement. Firstly, it does not need to be cleaned - the reinforcement of such a pipe is integral with the plastic. Secondly, the coefficient of expansion of the material is 5 times lower than that of conventional polypropylene.
Other advantages of polypropylene pipes, in addition to the ability to withstand elevated temperatures and pressures, include:
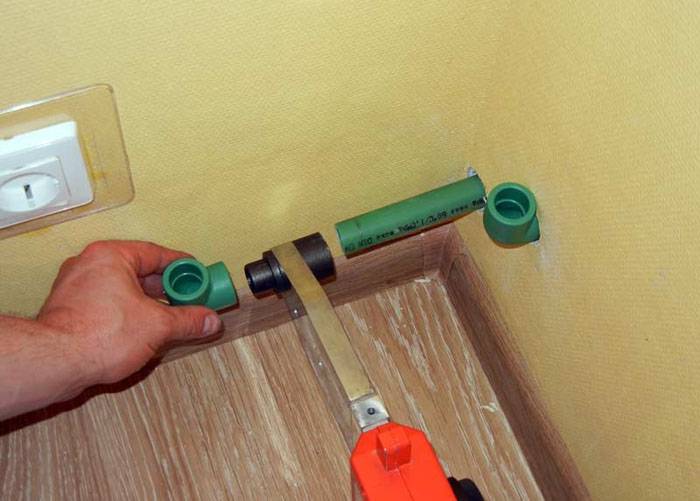
Reinforced-plastic pipes for heating: prices and features
Metal-plastic is used for heating at least as often as polypropylene. And its main advantages are about the same - lightness, compactness and the ability to withstand high temperatures of the working environment. Another additional plus is the small wall thickness, due to which the outer diameter of the pipes is smaller than that of polypropylene. In addition, during the installation of metal-plastic pipelines, it is not necessary to use special tools and equipment. And the aluminum layer and the coolant do not come into contact with each other, thus avoiding corrosion.
When choosing a pipe made of metal-plastic, you should know that two types of fittings are used for them - press and compression. The former are more suitable for heating. Compression elements can begin to leak over time, requiring periodic tightening.
Table 2. Cost of reinforced-plastic structures
| Parameter name | Picture | Diameter, mm | Price for 1 r.m., rub. |
|---|---|---|---|
| PE-RT HERZ |  | 16 | 110 |
| 20 | 120 | ||
| 26 | 240 | ||
| PE-RT / Al / PE-HD |  | 16 | 90 |
| 20 | 125 | ||
| 26 | 220 | ||
| PE-RT / Al / PE-RT |  | 16 | 95 |
| 20 | 100 |
Overview of metal products
When choosing ferrous metal as a material for heating pipes, you should be aware of its positive and negative qualities:
Stainless steel has many more benefits. Among them - resistance to corrosion, good appearance and the ability to withstand high pressure. And the pipes themselves can be used for both open and hidden wiring.
Table 3. Prices of steel pipes
| Picture | Diameter, mm | Price for 1 r.m., rub. |
|---|---|---|
 | Plain steel | |
| 15 | 60 | |
| 20 | 75 | |
| 32 | 120 | |
 | Stainless steel | |
| 15 | 140 | |
| 20 | 270 | |
| 25 | 400 | |
Using copper pipes and fittings for heating
Using copper pipes and fittings for heating, you can achieve maximum heating efficiency. It takes longer to mount these materials due to the need to obtain a soldered connection, but their reliability is much higher. Another limitation on the use of copper is the inability to use such pipes together with aluminum radiators. A copper pipe for heating is quite expensive - the price per meter starts from 250 rubles.
Table 4. Prices for copper pipes for heating
| Picture | Diameter, mm | Price for 1 r.m., rub. |
|---|---|---|
 | 15 | 250 |
| 22 | 450 | |
| 35 | 650 |
Polyethylene pipes: simplicity and durability
A polyethylene pipe is an excellent option for a heating system. First of all, due to the high strength of the material and the ability to withstand temperatures up to 90 degrees (for a short time - up to 100 degrees). And the service life of such products reaches 50 years. In addition, such a product can be mounted both hidden and open. Although in the latter case, the question may arise of how to decorate the heating pipe in the room (a large number of photos of possible options can be found on the Internet).
The PEX pipe system is assembled using special fittings. To do this, a ring or sleeve is put on the pipe, and its diameter is expanded with the help of special equipment. After that, the element is pulled first onto the fitting, then onto the sleeve. The result is an extremely strong bond.
Table 5. Plastic pipes for heating: sizes and prices
| Picture | Diameter, mm | Price for 1 r.m., rub. |
|---|---|---|
 | 20 | 30 |
| 25 | 50 | |
| 32 | 80 |
Video review: choosing a pipe for heating systems

Selection of pipe diameters
After determining the material of the pipelines, their diameter should also be selected. To do this, you should perform a small calculation, which uses such values as:
According to the norms, it is stipulated that for a room with a ceiling height of 2.5-3 m for heating 1 sq. m. area requires at least 0.1 kW of energy. Based on this value, the number and area of radiators in the premises is first calculated (the speed is taken to be 0.5–0.7 m / s). A correctly selected pipe can increase the efficiency of the entire heating system. Most often, its inner diameter, regardless of the results of the calculation, is taken at least 10 mm.
For a heating system with natural circulation of the coolant, the diameter will be larger - from 25–32 mm. The dimensions of the return pipeline are selected according to the parameter of the outlet boiler... If it has a diameter of 50 mm, the pipe should have the same indicator.
Related article:
What is the best choice for bimetallic heating radiators? In a special publication of our online magazine, we will provide a detailed overview of the advantages, prices and brands of bimetallic radiators.
Materials for insulating heating pipes
If necessary, to reduce heat loss and increase the efficiency of internal heating, you can use special insulation materials. Most often, insulation for heating pipes is chosen from the following list:
The choice of a suitable material largely depends on the location of the pipe to be insulated. We need insulation for communications located indoors, outdoors and underground. And each such method has its own characteristics.
Thermal insulation of pipelines in the room
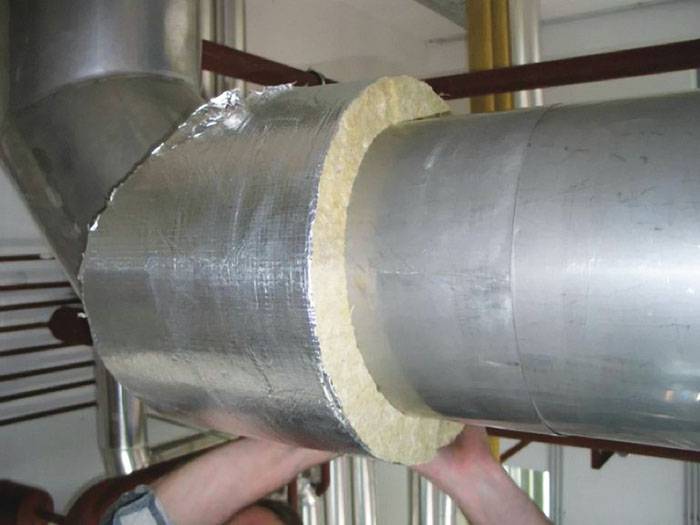
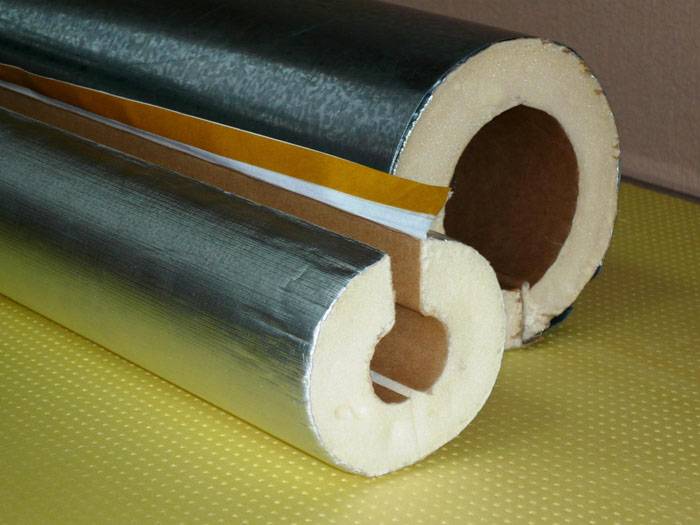
There is no need to insulate pipelines laid in an ordinary room. However, for that part of the heating system that runs through an unheated area, this procedure is mandatory. So, a feature of the pipes running through the basement is that there is no need for waterproofing. Therefore, here you can use materials such as polyurethane, foam and basalt wool to reduce the heat loss of the pipe.
Often in such cases, special covers made of expanded polystyrene are used. But the most popular of all the cheapest material is mineral wool. For insulation of the pipeline and the heating tank in the attic, materials are used that are resistant to strong heat. The need for this arises due to the temperature rise in the container above 100 degrees.
Protection of communications underground
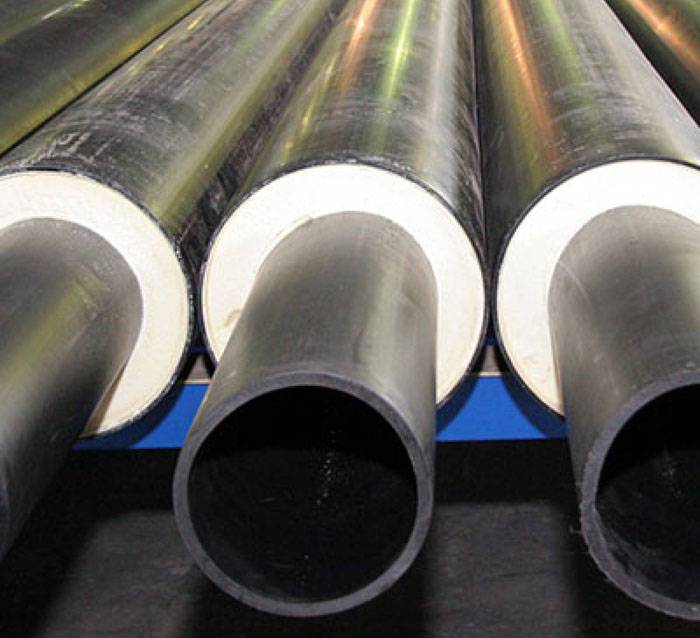
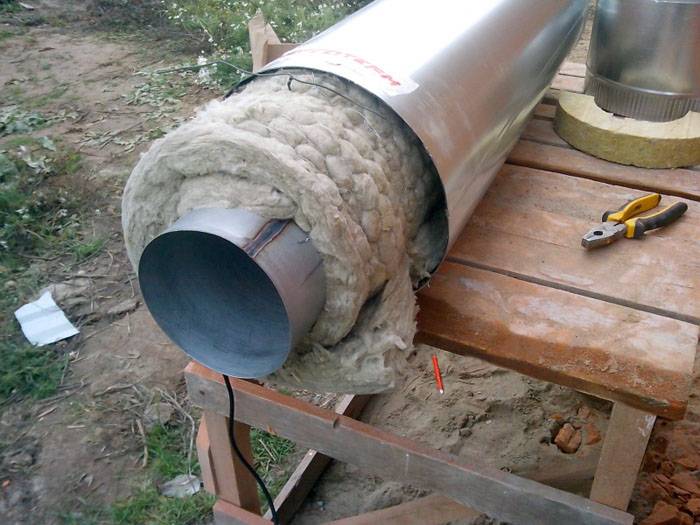
When laying district heating pipes underground, you should take into account such features as the level of freezing. And to protect communications from frost, they should be buried below this mark. In addition, it is undesirable for moisture to get on the insulation. Mineral wool, foam or expanded polystyrene are used as insulating material.
A popular method of frost protection is the use of structures that have already been insulated during manufacture. The configuration of these products may vary. But the common thing is the presence of a casing that protects the insulation.
Thermal insulation of pipes on the street
For insulation of district heating pipelines located outside, but above ground level, the following are most often used:
Insulation allows pipes to lose less heat and, as a result, increase the efficiency of the centralized system. The same actions ensure an increase in the temperature in the house. After all, it is precisely the insufficient thermal insulation that is one of the reasons for the insufficient heating of the premises in the winter.
Video review: comparison of types of thermal insulation for pipes