Adhesion: what it is, what is it for, how to improve it
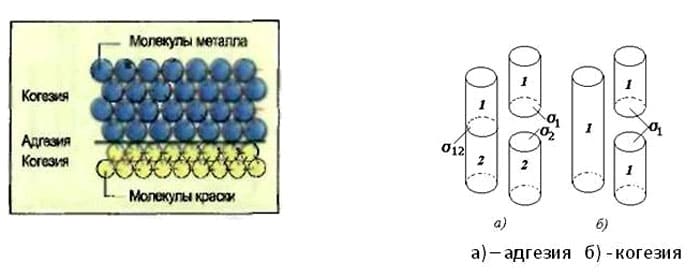
This is the adhesion of materials of different composition and structure, due to their physical and chemical properties. The term adhesion comes from the Latin word adhesion - adhesion. In construction, they give a more narrowly focused and specific designation of what adhesion is - the ability of decorative and finishing coatings (paintwork materials, plaster), sealing or adhesive mixtures to a strong and reliable connection with the outer surface of the base material.
Important! A distinction should be made between the concepts of adhesion and cohesion. Adhesion connects different types of materials, affecting only the surface layer. For example paint on a metal surface. Cohesion is a combination of materials of the same type, as a result of which intermolecular interactions are formed.
The content of the article
- 1 Adhesion, what is it - theoretical foundations
- 2 Adhesion properties of building and finishing materials
- 3 How is adhesion measured?
- 4 Factors that reduce the adhesion of materials
- 5 Methods for increasing adhesion
- 6 Ways to increase adhesion to various materials
- 7 Welding adhesion
- 8 Summing up
- 9 Video: what is adhesion
Adhesion, what is it - theoretical foundations
Adhesion is one of the key material properties in the following areas:
- Metallurgy - anti-corrosion coatings.
- Mechanics - a layer of lubricant on the surface of the elements of machines and mechanisms.
- Medicine - dentistry.
- Construction. In this industry, adhesion is one of the main indicators of the quality of work and the reliability of structures.
At almost all stages of construction, adhesion indicators for the following joints are monitored:
- paints and varnishes;
- plaster mixes, screeds and fillings;
- adhesives, masonry mortars, sealants, etc.
There are three basic principles for adhesive bonding of materials. In construction and technology, they manifest themselves as follows:
- Mechanical - adhesion occurs by adhesion of the applied material to the base.The mechanism of such a connection consists in the penetration of the applied substance into the pores of the outer layer or in connection with a rough surface. An example is painting the surface of concrete or metal.
- Chemical - the connection between materials, including those of different densities, occurs at the atomic level. To form such a bond, the presence of a catalyst is required. An example of this type of adhesion is soldering or welding.
- Physical - on the mating surfaces there is an electromagnetic intermolecular bond. May be caused by static electricity or permanent magnetic or electromagnetic fields. An example of use in technology is painting various surfaces in an electromagnetic field.
Adhesion properties of building and finishing materials
The adhesion of building and finishing materials is carried out mainly according to the principle of mechanical and chemical bonding. A large number of different substances are used in construction, the operational characteristics and specificity of the interaction of which are fundamentally different. We divide them into three main groups and characterize them in more detail.
paints and varnishes
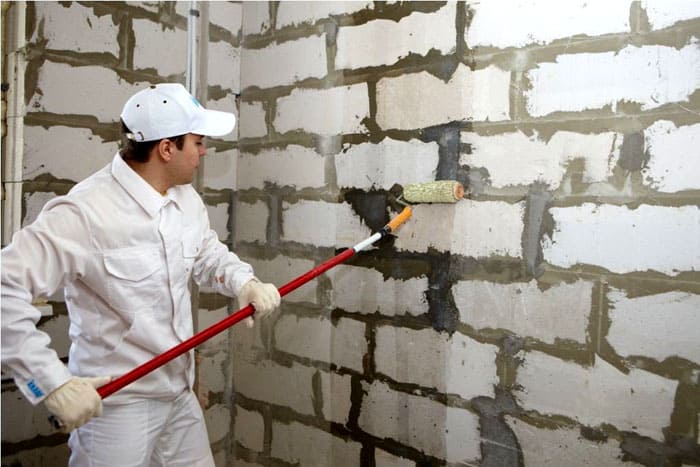
The adhesion of paintwork materials to the surface of the base is carried out according to the mechanical principle. At the same time, the maximum strength indicators are achieved if the working surface of the material is rough or porous. In the first case, the contact area increases significantly, in the second, the paint penetrates into the surface layer of the base. In addition, the adhesive properties of paintwork materials are increased due to various modifying additives:
- organosilanes and polyorganosiloxanes have an additional hydrophobizing and anticorrosive effect;
- polyamide and polyester resins;
- organometallic catalysts for chemical processes of paintwork materials hardening;
- ballast fine fillers (for example, talc).
Construction plasters and dry adhesives
Until recently, construction and finishing work was carried out using various solutions based on gypsum, cement and lime. Often, they were mixed in a certain proportion, which resulted in a limited change in their basic properties. Modern ready-made dry construction mixtures: starting, finishing and multi-finishing plasters and putties, have a much more complex composition. Additives of various origins are widely used:
- mineral - magnesia catalysts, water glass, alumina, acid-resistant or non-shrinking cement, microsilica, etc.
- polymeric - dispersible polymers (PVA, polyacrylates, vinyl acetates, etc.).
Such modifiers significantly change the following main characteristics of building mixtures:
- plastic;
- water retention properties;
- thixotropy.
Important! The use of polymer modifiers gives a more pronounced effect of enhancing adhesion. However, the formation of stable compounds of polymer films at the border of different types of materials (base - hardening plaster) is possible only at a certain temperature. This term is called the minimum film formation temperature - MTP. For different plasters, it can be different from + 5 ° C to + 10 ° C. To avoid delamination, the manufacturer's recommendations for temperature, both ambient and substrate, must be followed closely.
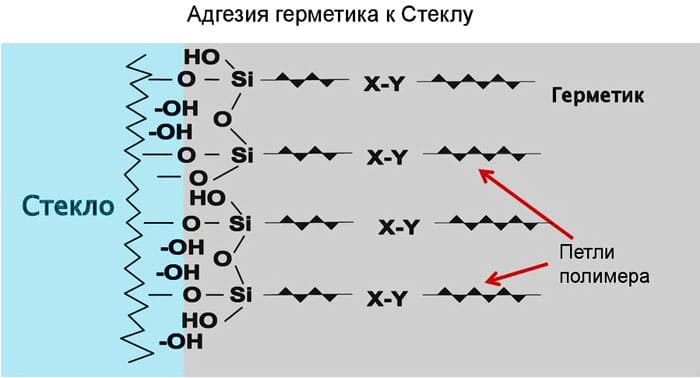
Sealants
Sealants used in construction are classified into three different types, each of which requires specific conditions for high strength adhesion to the substrate material. Let's consider each type in more detail.
- Drying sealants. The composition includes various polymers and organic solvents: styrene-butadiene or nitrile, chloroprene rubber, etc. As a rule, they have a pasty consistency with a viscosity of 300-550 Pa. Depending on the viscosity, they are applied either with a spatula or with a brush. After their application to the surface, a certain time is required for drying (evaporation of the solvent) and the formation of a polymer film.
- Non-drying sealants. They usually consist of rubber, bitumen and various plasticizers. Have limited resistance to high temperature, no more than 700S-800C, after which they begin to deform.
- Curing sealants. After their application, under the influence of various factors: moisture, heat, chemical reagents, an irreversible polymerization reaction occurs.
Of all the listed varieties, curing sealants provide maximum adhesion to microroughness of the substrate surface. In addition, they are resistant to high temperatures, mechanical and chemical influences. They have the optimal combination of stiffness and toughness, allowing them to maintain their original shape. However, they are the most expensive and difficult to use.
How is adhesion measured?
The technology for measuring adhesion, test methods, as well as all indicators of the strength of the connection of materials are indicated in the following standards:
- GOST 31356-2013 - Putties and plasters;
- GOST 31149-2014 - Paints and varnishes;
- GOST 27325 - Paintwork materials for wood, etc.
Information! Adhesion is measured in kgf / cm2, MPa (megapascals) or kN (kilonewtons) is a measure of the force that must be applied to separate the base and coating materials.
Whereas previously the adhesion characteristics of materials could only be measured in laboratory conditions, at the moment there are many instruments that can be used directly on the construction site. Most methods for measuring adhesion, both in the field and in the laboratory, involve the destruction of the outer covering layer. But there are several devices based on ultrasound.
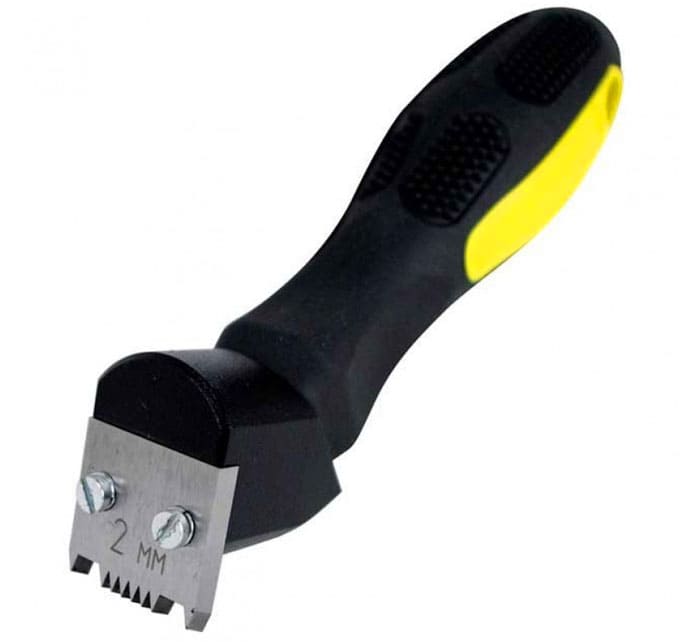
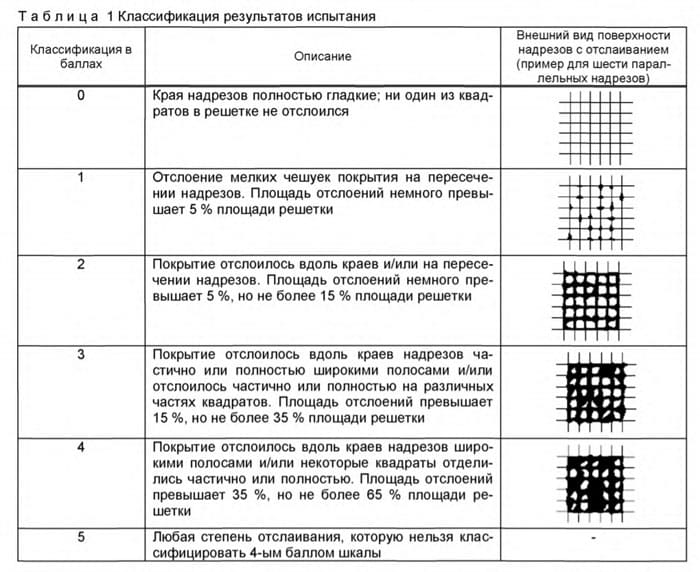
- Knife adhesion meter. It is used to determine the adhesion parameters by lattice and or parallel cuts. It is used for paint and varnish and film coatings up to 200 microns thick.
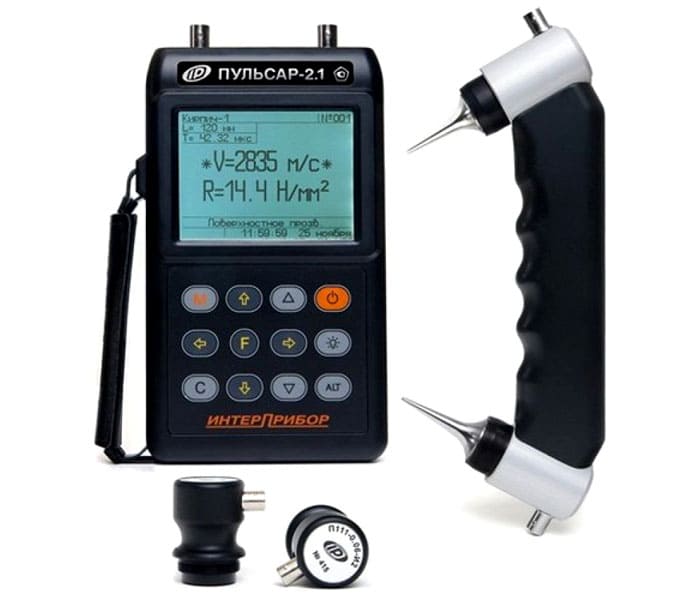
- Pulsar 21. The device detects the density of materials. It is used to detect cracks and delamination in concrete, both piece and monolithic. There are special firmwares and subroutines that, according to the adhesion density, allow you to determine the adhesion strength of various types of plasters to concrete surfaces.
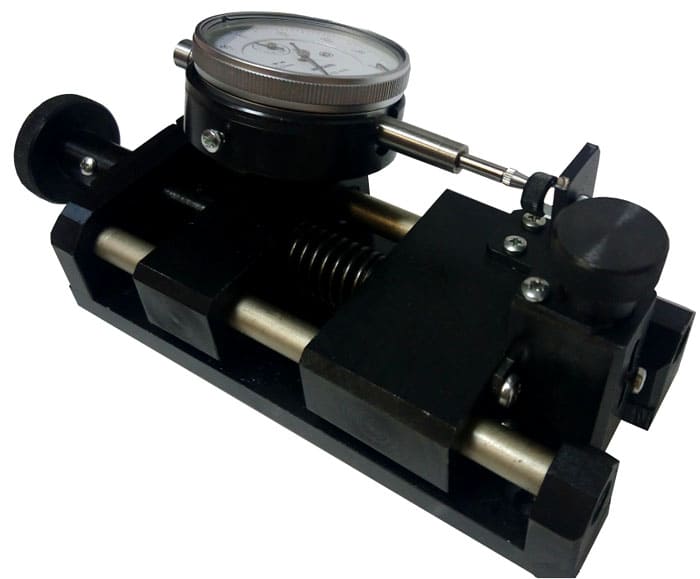
- SM-1U. It is used to determine the adhesion of polymer and bituminous insulating coatings by the method of partial destruction - shear. The measuring principle is based on detecting linear deformations of the insulating material. As a rule, it is used to determine the strength of the insulation coating of pipelines. It is allowed to use for quality control the application of bituminous waterproofing to building structures: walls of basements and basements, flat roofs, etc.
Factors that reduce the adhesion of materials
Various physical and chemical factors influence the decrease in adhesion. The physical temperature and humidity refers to the environment at the time of application of decorative, finishing or protective materials.Various contaminants, in particular, dust covering the surface of the base, also reduce the adhesive interactions. During operation, ultraviolet radiation can affect the strength of the connection of paints and varnishes.
Chemical factors that reduce adhesion are represented by various materials contaminating the surface: gasoline and oils, fats, acidic and alkaline solutions, etc.
Also, the adhesion of finishing materials can be reduced by various processes that occur in building structures:
- shrinkage;
- tensile and compressive stresses.
Information! A substance applied to a surface to increase the adhesion force between the substrate and the finishing material is called an adhesive. The substrate on which the adhesive is applied is called the substrate.
Methods for increasing adhesion
In construction, there are several universal ways to increase the adhesion of decorative finishing materials to the base surface:
- Mechanical - the surface of the base is roughened to increase the contact area. To do this, it is treated with various abrasive materials, notches are applied, etc.
- Chemical - various substances are added to the composition of the applied protective and finishing materials. These are, as a rule, polymers that form stronger bonds and give the material additional elasticity.
- Physicochemical - the surface of the base is treated with a primer that changes the basic chemical parameters of the material and affects certain physical properties. For example, a decrease in moisture absorption in porous materials, anchoring of a loose outer layer, etc.
Ways to increase adhesion to various materials
Let's take a closer look at the methods of increasing adhesion for various materials used in construction.
Concrete
Concrete building materials and structures are widely used in construction. Due to the high density and smoothness of the surface, their potential adhesive properties are quite low. To increase the strength of the connection of finishing compounds, the following parameters must be taken into account:
- dry or damp surface. Generally, the adhesion to a dry surface is higher. However, many adhesive mixtures have been developed that require pre-wetting of the substrate surface. In this case, you need to pay attention to the manufacturer's requirements;
- ambient and base temperature. Most of the finishing materials are applied to concrete surfaces at an air temperature of at least + 5 ° C ... + 7 ° C. At the same time, the concrete should not be frozen;
- primer. It is used without fail. For dense concrete, these are compositions with a filler of quartz sand (concretecontact), for porous concrete (foam, aerated concrete), these are deep penetration primers based on acrylic dispersions;
- adding modifiers. Ready-made dry plaster mixes already contain various adhesive additives. If the plaster is mixed on its own, then it is recommended to add to it: PVA, acrylic primer, instead of the same amount of water, silicate glue, which gives the finishing material additional moisture-repellent properties.
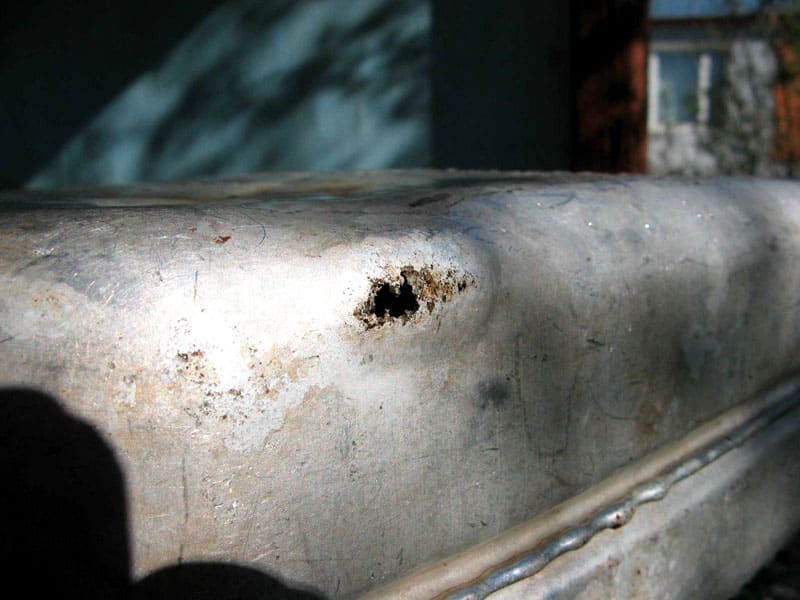
Metal
The method and quality of surface preparation play a key role in the strength of the connection of paints and varnishes with a metal surface. At home, it is recommended to do the following:
- degreasing - metal processing with various solvents: 650, 646, P-4, white spirit, acetone, kerosene. In extreme cases, the surface is wiped with gasoline;
- matting - processing of the base with abrasive materials;
- padding - use of special primer paints. They are sold complete with decorative paints of a certain type.
Important! The adhesion of lead, aluminum and zinc is much lower than that of cast iron and steel. The reason is that these metals form oxide films on their surface. Therefore, the peeling of paint and varnish coatings occurs along the oxide layer. It is recommended to color these materials immediately after removing the film by mechanical or chemical means.
Wood and wood composites
Wood is a porous surface with a lot of unevenness and does not experience any particular problems with the strength of the connection of finishing materials. But there is no limit to perfection, therefore, various technologies have been developed to improve adhesion in combination with maintaining the protective and decorative properties of the finish itself. Their use, for example, in combination with acrylic paints, significantly improves weather resistance, resistance to ultraviolet fading, and gives biological protection to the material. The surface of the wood is treated with a wide variety of primers, most often based on boron compounds and nitrocellulose.
Welding adhesion
Welding is one of the most durable methods of joining metal structures. This is the adhesion of the molecules of the two elements without the use of intermediate or auxiliary substances - glue or solder. This process takes place under the influence of thermal activation. The outer layer of the elements to be joined is heated above the melting point, after which intermolecular convergence and joining of materials occurs.
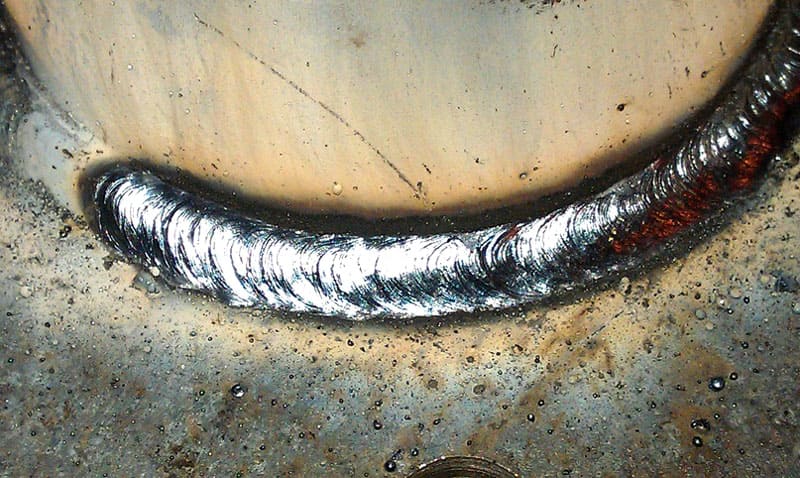

Electric welding seam. The connection of two parts by electric welding is adhesion, since the metal used in the electrode acts as an adhesive
The following factors can be an obstacle to high-quality adhesion during welding:
- the presence of oxide films. They are removed mechanically or chemically during surface preparation or disappear directly during the welding process under the influence of high temperatures or fluxes;
- inconsistency in the chemical composition of materials and electrodes. Particular attention should be paid to the presence and amount of silicon and carbon in the parts to be joined. For joining steels of different grades, it is recommended to use electrodes with a low diffusible hydrogen content;
- insufficient penetration depth, which directly depends on the current strength and the speed of movement of the electrode.
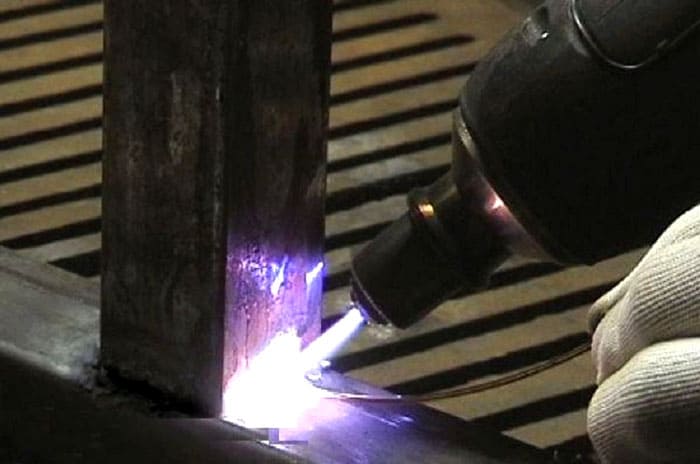

Gas or plasma welding of metal is cohesion, since the molecules of the two elements are connected as a result of the material melting
Summing up
Adhesion is one of the most important characteristics of many processes in modern construction, so new methods are being developed to increase it. Their use will provide greater durability to building structures and finishing materials, which ultimately will provide significant savings.