Heat shrinkage for wires - a reliable way to insulate live conductors
For the safe operation of the electrical facilities of industrial enterprises, housing and communal services, as well as other electrical networks, it is necessary to ensure reliable insulation of live parts of the equipment. To meet these requirements, various insulating materials and devices are used: insulating tape and caps, protective screens and heat-shrinkable tubes. Heat shrinkage for wires - the field of application of protective tubes, how to choose them and carry out the installation yourself, we will talk about this in the review of the homemaster.techinfolux.com/en/ editorial office.
The content of the article
- 1 What is heat shrinkage
- 2 Purpose and areas of application of the heat-shrinkable tube HERE
- 3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Heat Shrinkable Tube
- 4 Types of heat shrinkable tubing for wires
- 5 Basic and additional characteristics HERE
- 6 How tubes are labeled
- 7 How to choose a heat shrink tubing - our editorial team's recommendations
- 8 How to properly install a heat shrink tube with your own hands
- 9 At what price can you buy heat shrink tubing - an overview of offers
- 10 Video: heat shrink tubing application
What is heat shrinkage
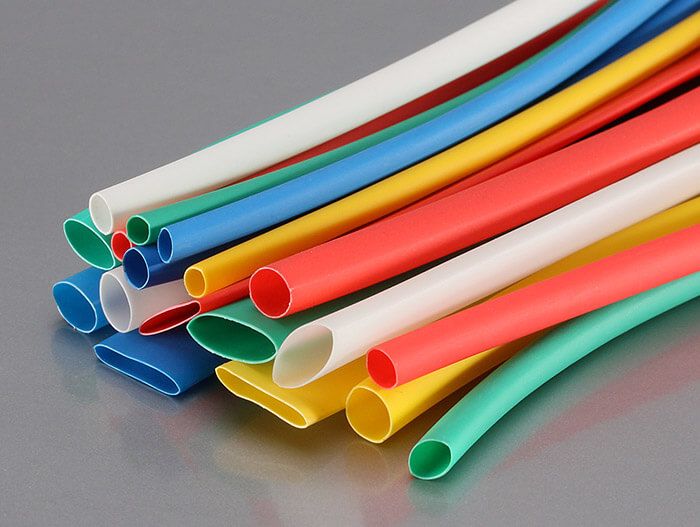
A heat-shrinkable tube (heat shrinkage) is a product made of thermoplastic types of plastic (polyethylene, polyester, fluoroelastomer and others), which, when heated, begin to "flow", coming into a stretching state, and when cooled, they harden. In this case, the shape given to such a product during heating is retained after it has cooled down. Heat-shrinkable tubes used in electrical networks must comply with GOST 17675-87 “Flexible electrical insulating tubes. General technical conditions ". Heat shrinking is easy to use, which determines a wide range of its uses.
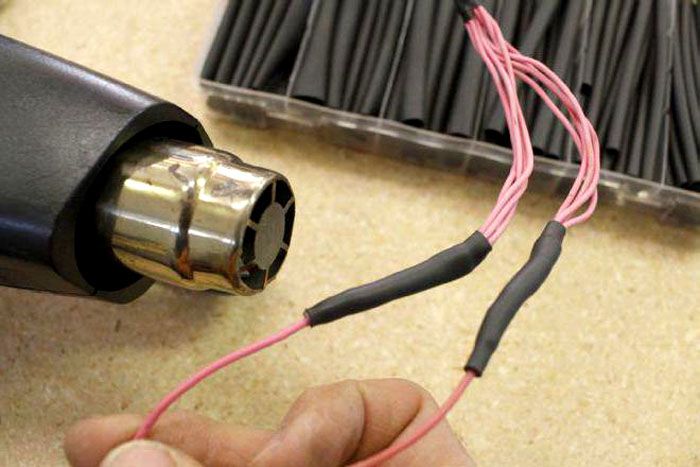
When installing such products, it is enough to put the tube on the prepared section of the wire, parts of a machine or other device, and then heat it up. Heating is carried out with a hair dryer, burner or an open flame source, if this is permissible for safety reasons. When heated, the heat shrinkage decreases in size and, shrinking, takes the form of an insulated object, after which it hardens.

Under the influence of high temperature, the heat shrinkage takes the shape and dimensions of the product on which it is placed, and retains them after cooling
Purpose and areas of application of the heat-shrinkable tube HERE
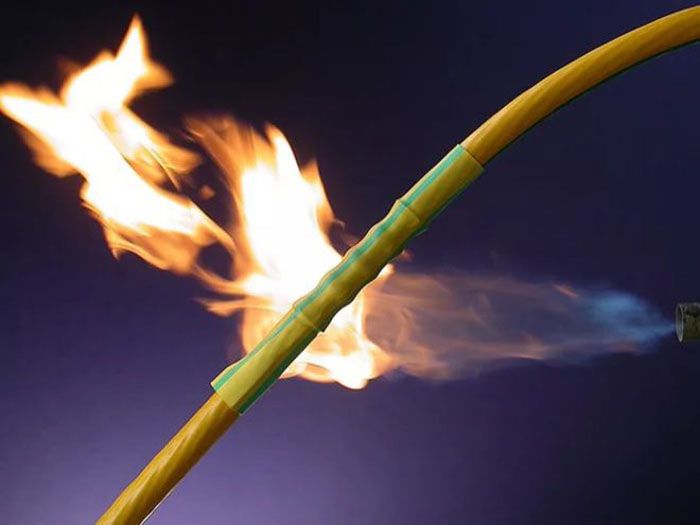
The ability of heat-shrinkable tubes (HERE) to threefold elongation, resistance to excessive heating and open flame, tensile strength and elasticity, as well as resistance to the effects of chemically active substances (acid, alkali) determine their purpose and applications. The main field of application of heat shrinkable wires is energy, where they are used to perform work:
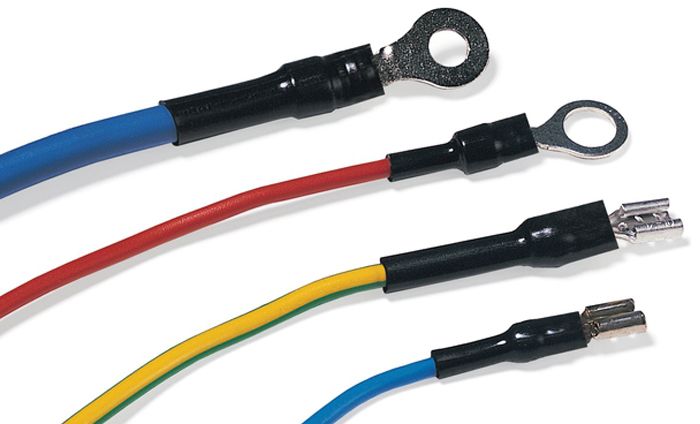
- insulation of live parts of equipment and conductive wires of wires;
- for the protection of the junction points of cable lines;
- when installing couplings and cable lugs;
- on wire marking.
In addition, heat-shrinkable tubes are used in various industries (automotive, chemical and others), as well as in transport.
With their help, it is carried out:
- repair and protection of structural elements and machine parts from external chemically active and aggressive influences (protection against corrosion);
- protection from thermal effects;
- imparting dielectric properties to locksmith tools (screwdrivers, wrenches, etc.);
- protection against abrasion in places where there should be no mechanical contact of units and mechanisms.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Heat Shrinkable Tube
Heat shrinkage, as, indeed, any product, has certain advantages and disadvantages that determine the possibilities and ease of use.
The advantages of such products include such indicators as:
- universality of application;
- ease of installation work;
- after cooling, HERE adheres tightly to the surface on which it was placed before heat treatment;
- in a solidified state, HERE increases rigidity, which gives the coated interface or insulation additional mechanical strength;
- long service life due to the ability to withstand external mechanical, thermal and chemical influences.
The disadvantages of heat shrink tubing are:
- impossibility of reuse;
- significant cost - when used as an insulating material (in comparison with conventional electrical tape).
Types of heat shrinkable tubing for wires
Heat-shrinkable tubes for wires differ in the material from which they are made, in geometric dimensions (diameter and wall thickness), as well as in the principle of mounting on a processed base:
- by material of manufacture. Currently, the industry produces a whole range of polymeric materials with thermoplasticity: polyethylene and polyester, fluoroelastomer and polyethylene terephthalate, polyvinylidene and polyvinyl chloride, as well as polymers of polyolefin composition. All these materials are used to some extent in the manufacture of heat-shrinkable tubes;
- according to the installation principle. According to this indicator, HERE is classified as glue and glueless. Adhesive heat-shrinkable tubes are distinguished by the fact that in their inner space there is a layer of adhesive that acts as a sealant after mounting the product on the surface to be treated;
- by wall thickness. The thickness of the walls HERE depends on the material from which they are made and the method of their installation. Thick-walled heat shrink tubes are produced without an adhesive layer, they are most in demand due to ease of use and cost, which is lower than models with a layer of adhesive.This type of product happens without suppressing combustion and not supporting it, which depends on the raw materials from which they are made;
- by diameter. The industry produces heat-shrinkable tubes of various diameters, which is regulated by GOST and corresponds to the range of wires and cables used for laying electrical networks and communications. Large-diameter shrinks are products up to 120 mm in size (before shrinkage), and the smallest HEREs have a diameter of 2 mm (before shrinkage). When marking products, the size before and after shrinkage is indicated, which is convenient for use. Technical characteristics for the most common standard sizes of heat shrinkage HERE are given in the following table.
Basic and additional characteristics HERE
The characteristics that determine the choice of a particular brand of HERE are the following values:
- Diameter before and after shrinkage.
- The type of material used, its flammability.
- Shrinkage coefficient - can be different for different brands HERE and be: 2 to 1/3 to 1/4 to 1/6 to 1.
- Wall thickness.
- The presence of an adhesive layer.
- Color scheme or transparency.
How tubes are labeled
Heat-shrinkable tubes of the TUT series are marked as follows. For example, the designation "TUTng - 2/1 0.4" stands for:
- HERE - an abbreviation indicates that this is a heat-shrinkable product;
- numbers through a fraction indicate the diameter of the tube before and after shrinkage;
- the numbers after the fraction indicate the wall thickness.
Additional designations inform:
- "Ng" - does not support combustion.
How to choose a heat shrink tubing - our editorial team's recommendations
On the market of insulating materials, there is a fairly wide selection of models of heat shrinkable tubes, this is the HERE series, about which it was written above, as well as brands "DERAY" (series: PBF, I, H, LSB), "RADPLAST" (series: T-1, T-2, T-4) and a whole range of series and modifications. The choice of a specific brand should be approached responsibly, because this will help to secure the operation of electrical installations and other equipment, extend their service life.
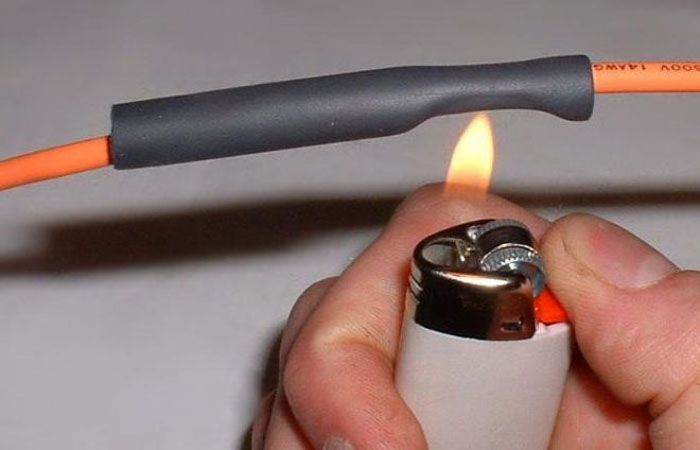

Using a gas lighter is the easiest way to install heat shrink, however, it is only available on small sizes of similar products
Sales consultants at the points of sale of such materials, as well as advice from our editorial staff, can help to understand this issue, which can be formulated as follows:
- the diameter of the tube after shrinkage should be less than the diameter of the product on which it is mounted, which will ensure reliable contact between them;
- to prevent damage to the walls of the tube, its diameter before shrinkage must be greater than the landing size;
- the diameter after shrinkage should be less than 20% of the bore diameter and 10% more - in the state before installation work;
- the surface on which the heat shrinkage is being installed must be cleaned of dirt and foreign particles;
- the type of tool used when performing work must correspond to the material from which the tube is made (melting temperature) - hair dryer, burner, etc.;
- work on heating the surface of the tube should start with casing around the circumference in the central part of the product, after which it should be heated from the middle towards the ends, which will ensure the absence of bubbles and folds as a result of the operations performed;
- it is impossible to fix the heat source in one place for a long time, becausethis can lead to burning of the tube surface;
- when cutting heat shrinkage, it must be remembered that after heat treatment, it shrinks along its length;
- to ensure tightness wire connections or insulation of other structures, you should use grades that include an adhesive layer.

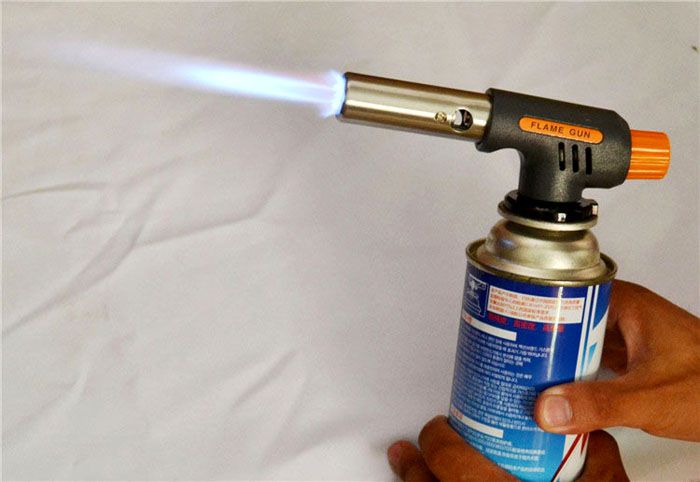
The use of burners is most effective when installing couplings and terminations of power electrical cables
How to properly install a heat shrink tube with your own hands
In order to carry out the correct installation of the heat-shrinkable tube, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to this issue even at the stage of preparing the work.
At the preparatory stage it is necessary:
- select the required standard size and brand of heat shrinkage;
- decide on the amount of material required;
- study the market for offers that exist in the user's place of residence or work;
- prepare the necessary tool.
Special attention should be paid to the selection and preparation of the instrument, because for different brands of pipes, the working temperature is different and can reach several hundred degrees, which is impossible to create with such devices as a household hair dryer or a gas lighter.
The following are used as a professional tool:
- construction hair dryer;
- portable gas burner;
- gas soldering iron;
- propane burner;
- infrared burners.
When the preparatory work has been completed, you can proceed with the installation. The heat shrink tubing installation process is performed in the following sequence.
When performing work, you must remember that:
- if the tube is of considerable length and large diameter, then heating must be carried out from its middle in the direction of the edges, while initially it should be deposited in a circle in the middle;
- if it is not clear whether a piece of heat shrinkage is enough in length, then it is necessary to start heating from one of the ends, at which the heat shrinkable tube should end (wire tip, communication plug, etc.);
- if the tube is mounted on a metal surface with good thermal conductivity, then before starting work, such a surface should be preheated;
- if there are sharp edges on the surface to be coated, then they should be removed;
- if the length of the heat shrinkage is insufficient, it must not be stretched, because this will lead to a decrease in strength and dielectric characteristics.
Taking into account these requirements and the recommendations of our editorial staff, any user can easily install the heat-shrinkable tube on their own.
At what price can you buy heat shrink tubing - an overview of offers
On the market of insulating dielectric materials, there is a fairly wide selection of heat shrinkable tubes from various manufacturers, which allows you to choose the desired model in accordance with the technical characteristics, purpose and operating conditions of the products on which they are installed. You can buy heat shrinkage for wires in lighting stores and electrical products, specialized organizations dealing with power supply and low-current communications, as well as on Internet resources, where companies selling similar products are also represented.

The heat-shrinkable tube is sold in sets with a different number of colors and different lengths, as well as in coils, rolls and boxes of the same color in linear terms
The following table shows the price for some standard sizes of the heat-shrinkable tube when sold via the Internet, as of the II quarter of 2018.
In order to get acquainted with the cost of a particular brand and a certain standard size, you need to contact a trade organization that sells such a product, or use a search program on the Internet.
Related article:
Terminals for connecting wires. In the publication we will consider the pros and cons of using terminals, requirements, varieties, selection criteria, an overview of popular manufacturers, how to properly connect aluminum and copper wire.