Zeroing and grounding: what is the difference and which is better
Every day, at home and at work, we have to deal with electricity, which makes human life more comfortable. But, despite the benefits that the use of electricity gives us, it still poses a certain danger, for example, electric shock. To avoid this, electrical safety requirements have been developed and special protective measures are taken. These measures include grounding and grounding. What is the difference between them and is there any, we will figure it out in this article.
The content of the article
- 1 Basic requirements for electrical safety
- 2 What is grounding, principle of operation and device
- 3 When and where grounding is applied
- 4 Basic methods of grounding
- 5 What is grounding
- 6 Is it possible to do grounding in an apartment using grounding
- 7 What is the difference between grounding and zeroing
- 8 Requirements for grounding and neutralization
- 9 Let's sum up
Basic requirements for electrical safety
The main requirement for household electrical appliances is safety. To a greater extent, this applies to devices that come into contact with water, because even a minor defect in electrical wiring equipment can be fatal to the user. To protect yourself and those around you, you need to keep the power grid and equipment in good condition and regularly audit them.To exclude the possibility of fire due to faulty wiring and electric shock, protective devices (RCDs) must be installed.
In accordance with the basic rules of electrical safety:
- The device of temporary electrical wiring is not recommended.
- The connection of the wires must be done by welding, crimping, clamps or terminal blocks... Check the quality and tightness of the wiring connections regularly.
- In areas with high humidity, use only certified waterproof devices.
- Electrical outlets and switches should be located from heating pipes, gas and water supply at a distance of at least 500 mm.
- Check the wiring and electrical equipment regularly.
- Do not use any kind of electrical equipment without a protective cover.
- Do not use home-made electrical appliances and do not repair faulty electrical equipment yourself.
This is just a short list of electrical safety requirements. More information on safety rules can be found in various regulations and special literature on electricity, which are now easily found on the Internet.
What is grounding, principle of operation and device
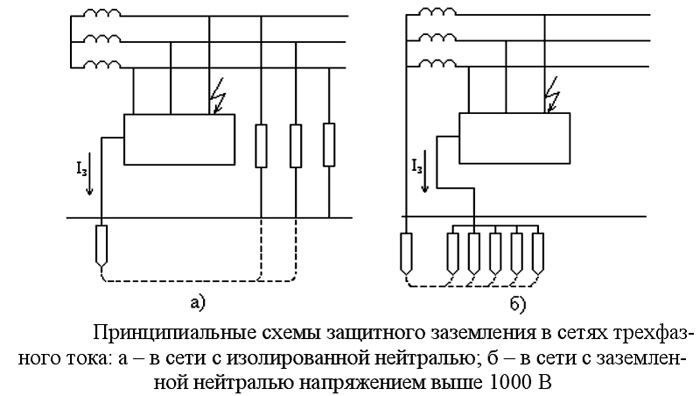
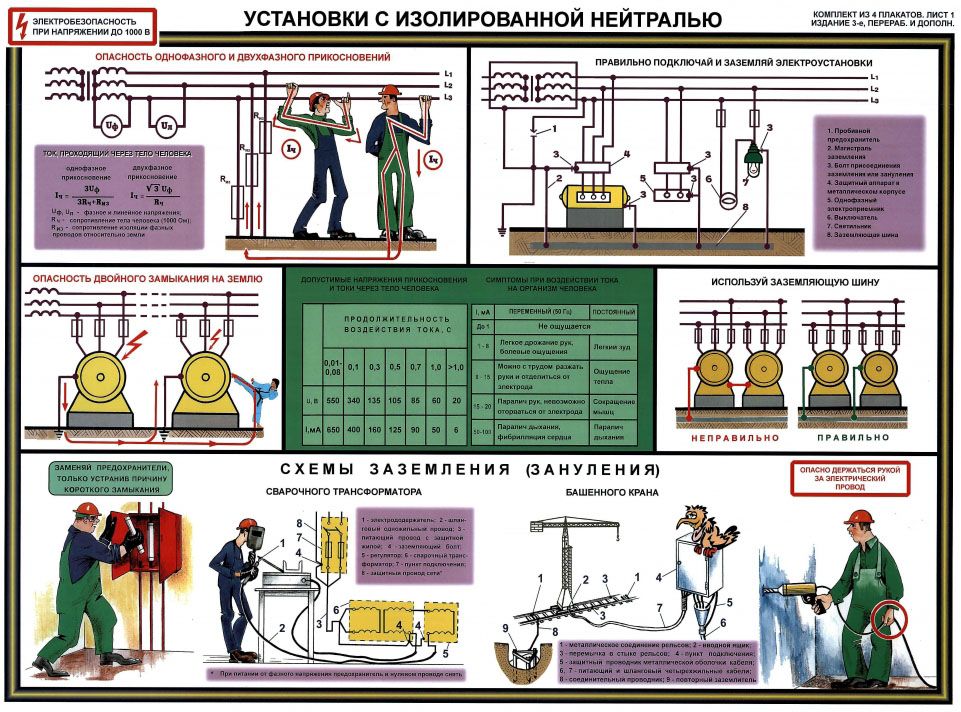
When creating an electrical network, in rooms for various purposes, it is required to create protection that will prevent possible electric shock. To avoid this, a grounding device is performed. In accordance with PES clause 1.7.53, grounding is performed in electrical equipment with a voltage of more than 50 V AC and 120 V DC.
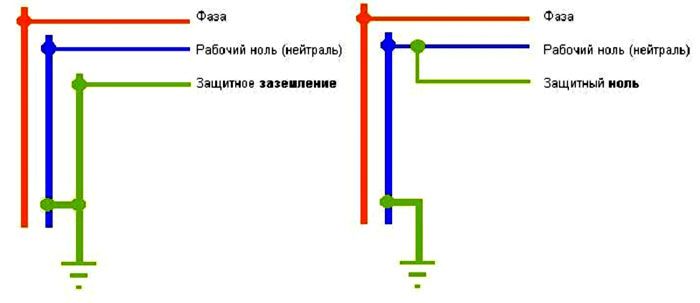
Grounding is the deliberate connection of non-current-carrying metal parts of electrical installations (which may be energized) to earth or its equivalent. This protective measure is designed to exclude the possibility of electric shock to a person when shorting to the equipment case.
Operating principle
The principle of operation of protective grounding is:
- reducing the potential difference between the grounded element and other conductive objects with natural grounding to a safe value;
- current drain in case of direct contact of the equipment to be grounded with the phase conductor. In a well-designed electrical network, the occurrence of a leakage current causes an instantaneous trip of a residual current device (RCD).
From the above it follows that grounding is more effective when used in conjunction with an RCD.
Grounding device
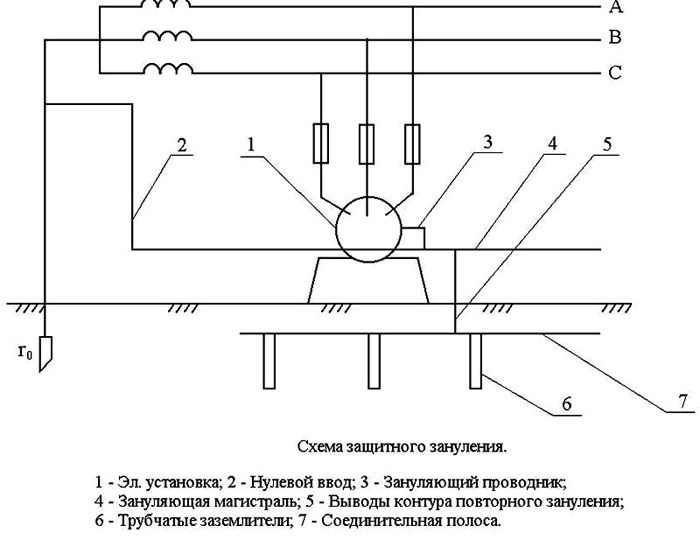
The design of the grounding system consists of an earthing switch (a conductive part that has direct contact with the ground) and a conductor that provides contact between the earthing switch and non-current-carrying elements of electrical equipment. Usually, a steel or copper (very rarely) rod is used as a ground electrode; in industry, this is usually a complex system consisting of several elements of a special shape.
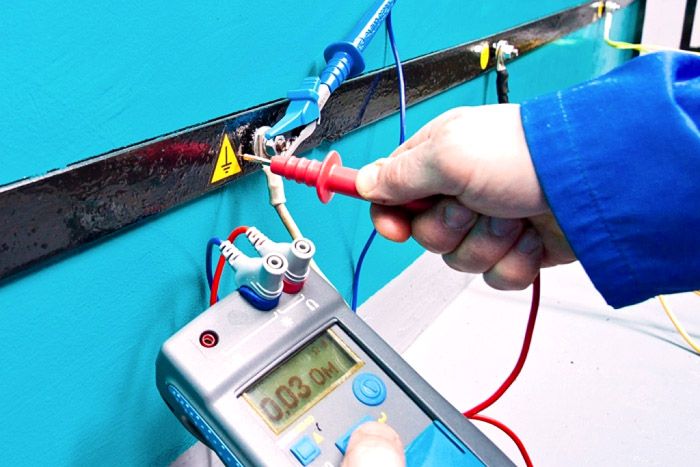
The efficiency of the grounding system is largely determined by the value of the resistance of the protective device, which can be reduced by increasing the useful area of the ground electrodes or increasing the conductivity of the medium, for which several rods are used, the level of salts in the ground rises, etc.
The grounding device is ...
Above, we examined in general terms what protective grounding is. However, it is worth mentioning that the ground electrodes used in the system differ into natural and artificial.
As grounding devices, it is primarily preferable to use such natural grounding conductors as:
- water pipesin the ground;
- metal structures of buildings and structures that have reliable contact with the ground;
- artesian casing wells;
- metal sheaths of cables (the exception is aluminum).
Important! It is forbidden to use pipelines with gas and flammable liquids, as well as heating mains as a grounding element.
Natural earthing switches must be connected to the protective system from two or more different points.
In the role of an artificial ground electrode can be used:
- steel pipe with a wall thickness of 3.5 mm and a diameter of 30 ÷ 50 mm and a length of about 2 ÷ 3 m;
- steel strips and corners with a thickness of 4 mm;
- steel rods up to 10 meters or more in length and 10 mm in diameter.
For aggressive soils, it is necessary to use artificial ground electrodes with high corrosion resistance and made of copper, galvanized or copper-plated metal.So, we figured out what is the definition of the concept of an artificial and natural ground electrode system, now we will consider when grounding is applied.
This video clearly explains what protective grounding is:
When and where grounding is applied
As already mentioned, protective grounding is intended to eliminate the likelihood of electric shock to people in the event of voltage supply to the conductive parts of the equipment, that is, when shorting to the case.Metal non-current-carrying elements of electrical installations are equipped with protective grounding, which, due to a probable breakdown of the insulation of wires, may be energized and harm the health and life of people and animals in the event of their direct contact with faulty equipment.
Power grids and equipment with voltages up to 1000 V are subject to grounding, namely:
- alternating current;
- three-phase with insulated neutral;
- two-phase, isolated from earth;
- direct current;
- current sources with an isolated winding point.
Also, grounding is necessary for power grids and electrical installations of direct and alternating current with voltages above 1000 V with any neutral or midpoint of the current source winding.
Basic methods of grounding
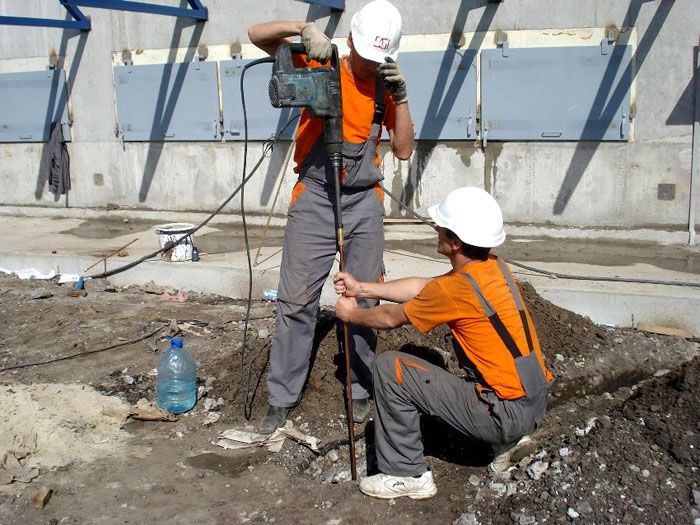
When installing a grounding system, vertical metal rods are usually used as a ground electrode. This is due to the fact that horizontal electrodes have increased electrical resistance due to their shallow burial depth. Steel pipes, rods, corners and other rolled metal products with a length exceeding 1 meter and having a relatively small cross section are almost always used as vertical electrodes.
There are two main methods for installing vertical grounding electrodes.
Related article:
Electricity is capable not only of creating comfortable living conditions, but also carries a certain danger. To reduce the likelihood of this hazard occurring, DIY grounding in a private house 220V... How to do it - read the publication.
Several short electrodes
In this version, several steel corners or rods 2-3 meters long are used, which are connected together using a metal strip and welding. The connection is made at the surface of the earth.The earthing switch is installed by simply driving the electrode into the ground using a sledgehammer. This method is better known as "corner and sledgehammer".
The minimum permitted cross-section of grounding electrodes is given in the PUE, but most often the corrected and supplemented values from the technical circular No. 11 "RusElectroMontazh". In particular:
- for a corner and a strip of black steel with a cross section of at least 150 mm2 and a wall thickness of 5 mm;
- for a steel rod with a diameter of at least 18 mm;
- for steel pipes with a wall thickness of 3.5 mm and a minimum diameter of 32 mm.
The advantages of this method are simplicity, low cost and availability of materials and installation.
Single electrode
In this case, an electrode in the form of a steel pipe (usually a single one) is used as a ground electrode, which is placed in a deep hole drilled in the ground. Drilling the soil and installing the electrode requires the use of special equipment.
An increase in the area of contact of the ground electrode with the ground is provided by a greater depth of the electrode installation. Moreover, this method is more effective in comparison with the previous version, with the same total length of the electrodes, due to the achievement of deep soil layers, which, as a rule, have a low specific electrical resistance.
The advantages of this method include high efficiency, compactness and seasonal "independence", i.e.due to winter freezing of the soil, the specific resistance of the ground electrode practically does not change.
Another way is to lay a ground electrode system in a trench. However, this option requires large physical and material costs (more material, digging trenches, etc.).
Having figured out how it works and why grounding is needed, now the second question of our article is, namely, what is grounding, what is it for and how it differs from grounding.
What is grounding
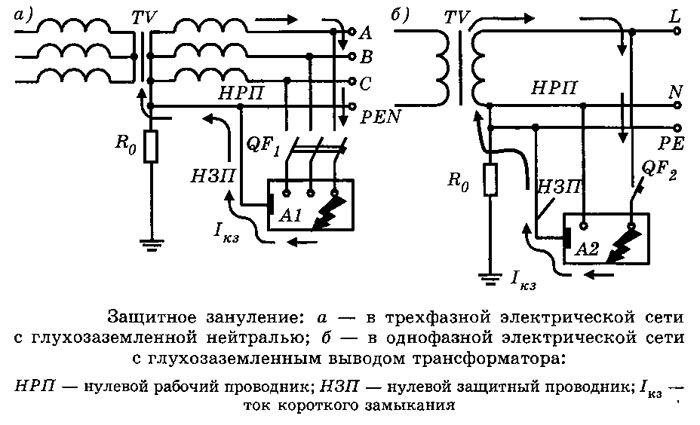
The term grounding denotes the deliberate connection of open non-current-carrying conductive parts of the power grid and equipment with a dead-earthed point in single- and three-phase DC and AC networks. Zeroing is carried out for the purpose of electrical safety and is the main protective means against energization.
Operating principle
A short circuit in the power supply network occurs when a live phase wire contacts the device body, connected to zero. The current rises sharply, and protective devices are triggered, cutting off power from the faulty equipment. According to the rules, the response time of the RCD to disconnect the faulty power supply should not exceed 0.4 seconds. For this, it is necessary that the phase and zero have an insignificant value of resistance.
Related article:
 Have you ever heard the acronym RCD? What it is you will find out by reading the review to the end. In short, I would like to add that this device is able to protect housing and all its inhabitants from emergencies associated with electricity.
Have you ever heard the acronym RCD? What it is you will find out by reading the review to the end. In short, I would like to add that this device is able to protect housing and all its inhabitants from emergencies associated with electricity.
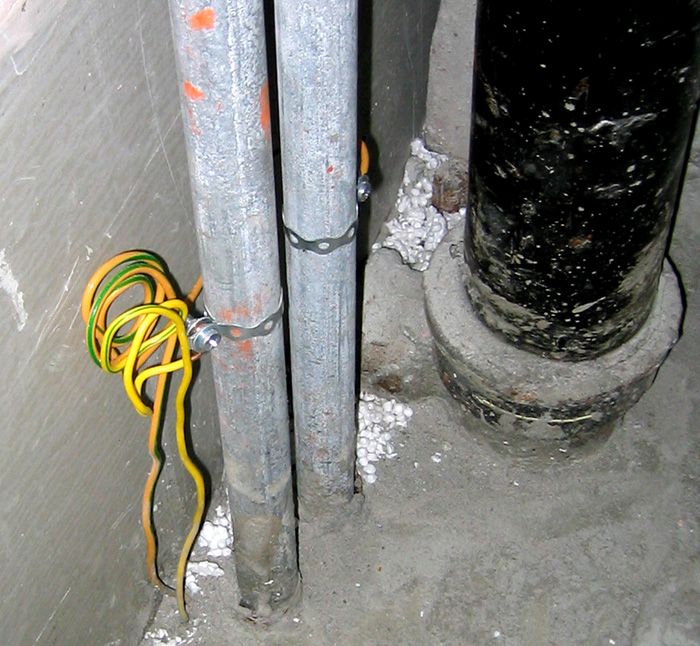
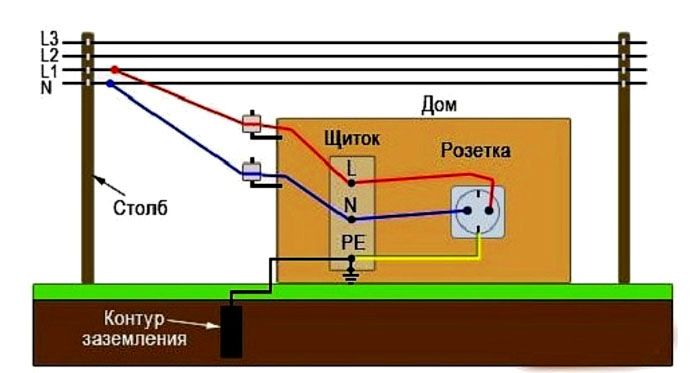
To create grounding in a single-phase network, as a rule, use the third (unused) wire of a three-core cable. To create good protection, it is required to ensure a high-quality connection of all elements of the grounding system.
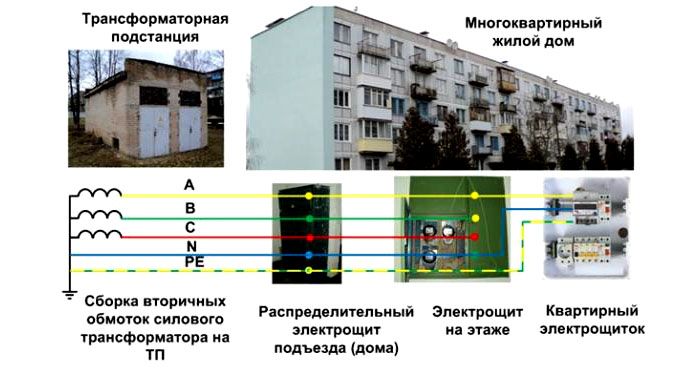
Device
The grounding system, for example, in an apartment building, begins with a grounded power transformer, from which a neutral with a three-phase line comes to the main distribution board (MSB) of the building. Next comes wiring for floor switchboards... A working zero is created from the neutral, which, together with the phase wire, forms the usual single-phase voltage.
Directly the grounding itself to protect the power grid and equipment is created in the shield using a conductor connected to the grounded neutral. You should be aware that it is forbidden to install switching devices between zero and neutral (automatic machines, packets, switches, etc.).
Where is the zeroing scheme used?
According to the PES requirements, protective grounding must be equipped with:
- one- and three-phase AC networks with a grounded outlet and voltage up to 1000 V;
- DC power grids with a midpoint grounding and voltage up to 1,000 V.
Grounding cannot save you from electric shock like grounding. This protective circuit simply cuts off the voltage supply in the event of a short circuit and disconnects the local power grid.
Is it possible to do grounding in an apartment using grounding
We already know what grounding and neutralization are and we will try to find out whether it is possible to do grounding using a grounded zero located in the electrical panel. The fact is that many people far from electrical engineering ask this question and often make unforgivable mistakes by doing this.
First, it is prohibited by PES. The fact is that if, for example, during installation work, for any reason, you mix up the phase and zero, and besides, bring the zeroing to a working zero, then you can expect the most unpleasant situations. When the electrical equipment is turned on to the network, the case will be energized and the person is electrocuted, since the protective operation of the RCD will not occur.
To create a protective grounding in the storey electrical panel, a separate bus is allocated, which is connected to the dead-grounded neutral. And it is best not to do these work yourself, but to entrust it to a specialist with knowledge in electrical engineering.
The video shows how to create a zeroing if it is not in the floor switchboard:
What is the difference between grounding and zeroing
It should be said right away that despite the fact that grounding and grounding are protective measures, they have differences in principle of operation and purpose.Grounding is a more effective and reliable way of protection than grounding, since it allows you to quickly equalize the difference between the potentials to the required value. Also, grounding has a simpler design and easier to install, and you just need to follow the instructions for its device. In addition, this protective circuit does not depend on the phase of the connected equipment. Grounding options are varied, and this allows you to choose a specific type for each specific case
Protective neutralization is a protective measure that, in the event of a network failure, simply provides an instantaneous interruption of the supply voltage from the mains by means of the RCD tripping. To create grounding and connect equipment requires experience and certain knowledge in electrical engineering. All installation work, especially the determination of the zero point, must be performed correctly, otherwise, in an emergency, electric shock may occur.
Having figured out what grounding and neutralization are, many people prefer to use both methods. However, grounding is mandatory for the installation of household and industrial networks, as well as the operation of equipment.
To better understand what is the difference between grounding and earthing, we suggest watching this video:
Requirements for grounding and neutralization
Grounding is a more serious protective measure than grounding. This circuit requires the creation of a separate low-resistance bus, which is connected to a ground electrode dug into the ground and equipped in accordance with standards. All requirements for grounding, its elements and arrangement are spelled out in the PES and GOST 12.2.007.0.
In the industrial sector, grounding is subject to:
- electric drives;
- electrical equipment housings;
- metal structures of buildings;
- shielded braid of low-voltage electric cables;
- switchboard enclosures and similar structures.
There are more loyal requirements for zeroing, namely:
- neutral and phase conductors are selected in such a way that, during a breakdown, a current sufficient for the operation of an RCD or other protective mechanism occurs;
- the grounding conductor from the device to the grounded neutral must be continuous, that is, it must not contain any switching devices in the circuit.
Let's sum up
Ensuring the safety of life and health is the primary task of the state, society and, naturally, the person himself. To do this, you must strictly adhere to the established rules, instructions and requirements. One of the factors hazardous to human health is electricity, therefore it is very important to ensure sufficient electrical safety at work and at home with the help of certain measures and protective technical means.
If you still have questions on this topic or have new ones, then write in the comments, our team will try to answer them.