The choice of pipes for sewage: types, sizes, features of use
Pipes are one of the main structural elements sewerage systems... Until recently, they were too cumbersome and heavy to be installed by the DIYer. But, due to the widespread use of polymers, the nomenclature of materials and standard sizes of pipes and fittings has expanded significantly. New technologies and tools have appeared for the reliable connection of pipeline joints. However, users have a new problem - the choice of pipes for the sewage system by type and size, and most importantly, by material of manufacture. In this article, we will list the technical and operational characteristics, advantages and disadvantages of the main types of sewer pipes. We will give advice on how to choose the diameter in accordance with the standards, as well as make a small overview of the most reliable, proven manufacturers.

There is a wide variety of sewer pipes, and it is rather difficult to choose the best option in each specific case.
PHOTO: strong-k.ru
The content of the article
Varieties of sewer pipes requirements for them
There are several criteria by which the selection of material for sewer pipes is made:
- High strength and carrying capacity. Sewer cleaning the case is extremely unpleasant. Only a pipe break can be worse. To avoid systematic (frequent) maintenance and emergency situations, it is necessary not only to carry out the installation in accordance with the current regulations, but also to select the appropriate diameter.
- Durability. The service life of the sewer system directly depends on the pipe material. In particular, its ability to withstand aggressive external influences.
Based on the listed requirements, you can specify a list of performance characteristics that the pipe material and the product itself must meet:
- high resistance to static pressure and impact deformation;
- the inner surface should be smooth and durable, especially resistant to abrasion;
- minimum coefficient of thermal deformation;
- light weight;
- simple technologies and high installation reliability;
- affordable cost.
Steel
Steel pipes used in sewer systems are made from so-called black steel - GOST 8732–78 and GOST 10704–91. They are connected by welded or threaded method. As a rule, the range of sizes is limited to products of medium and large diameters from 100 mm and above. They are used in pressure sewer (main) networks, for transportation of household and industrial wastewater.
Benefits:
- high-strength;
- wide range of operating temperatures;
- relatively easy to process (with special tools).
Disadvantages:
- high susceptibility to corrosive processes;
- considerable weight, especially with an external anti-corrosion and thermal insulation coating.
Cast iron
Until recently, cast iron pipes were the most common in both industrial and domestic sewer networks. Like steel, they are produced in medium to large diameters from 100 mm to 400 mm. Standard length - 3000 mm, wall thickness - from 4 mm (GOST 6942–98). They are divided into two types by functionality:
- SMU - both ends smooth, welded or coupled.
- SME - has a detachable connection, one end with a socket, the other is smooth.
Benefits:
- highest strength;
- durability - the declared service life of 50 years is often exceeded without negative consequences;
- no special equipment is required for the installation of SME products.
Disadvantages:
- high price;
- heavy weight - in most cases, construction lifting equipment is needed for installation in the working position;
- high labor intensity of joining joints;
- rough inner surface contributes to the adhesion of dirt and the formation of blockages;
- cast iron is a rather fragile material. It can crack if hit hard.
Important! Pay attention to the modern version of the sewer pipes made of magnesium modified cast iron - VChShG. This material is more ductile and resistant to cracking, and has a higher corrosion resistance.

Traditional pipes for a sewer riser in an apartment building are made of cast iron
PHOTO: nord-camping.ru
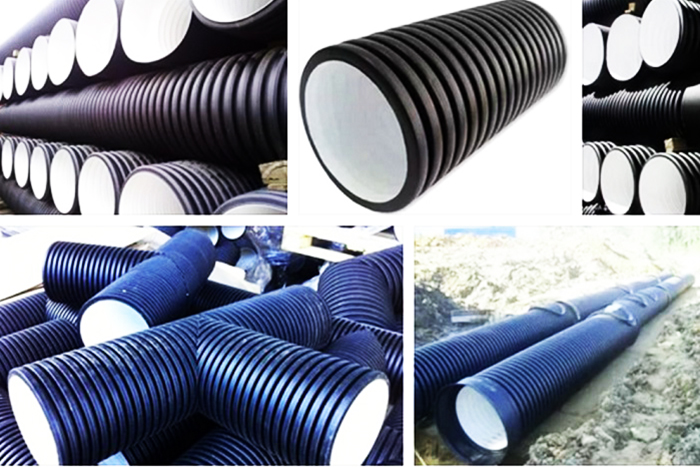
Polyethylene
Conventional medium-pressure polyethylene (PSD) is of little use for the production of sewer pipes. It has a high coefficient of thermal linear expansion, as well as a narrow operating temperature range of -40 ° C ... + 40 ° C. Therefore, it is recommended to use pipes made of low pressure polyethylene - HDPE and high pressure - LDPE for domestic sewage. Despite the different production methods, the performance characteristics and the advantages and disadvantages of these two types of polyethylene are quite similar. They are produced in a wide range of standard sizes for the internal system 50-110 mm free-flow, for the external system up to 400 mm. Pressure ones withstand from 5 to 20 atmospheres. Technical requirements GOST 22689.2-89.
Benefits:
- long operational period. Some manufacturers claim up to 100 years old;
- absolute immunity to any type of corrosion processes;
- resistance to aggressive environments;
- resistance to water hammer;
- low coefficient of linear expansion under the influence of temperature;
- light weight.
Disadvantages:
- mediocre resistance to high temperatures. The exception is cross-linked polyethylene, which can withstand up to + 400 ° C;
- loss of properties under the influence of ultraviolet radiation;
- average strength characteristics.
Polypropylene
Polypropylene pipes They are characterized by increased resistance to biological corrosion and aggressive chemicals. Products of small diameter up to 100 mm are used for internal systems.For the external pipeline, special two-layer structures with an external corrugated layer (diameter up to 1200 mm) are used, which gives the product additional strength. Regulatory requirements TU 4926-002-88742502-00.
Benefits:
- high viscosity of the material, as a result of which the products do not lose their integrity during thermal deformation;
- resistance to high temperatures. Polypropylene can withstand operating temperatures up to 100 ° C;
- resistance to aggressive household chemicals up to acids and alkalis of high concentration;
- diffusion resistance - substances do not pass through the wall.
Disadvantages:
- susceptibility to ultraviolet light - outdoor installation prohibited;
- high elasticity requires wall thickening or stiffening ribs.
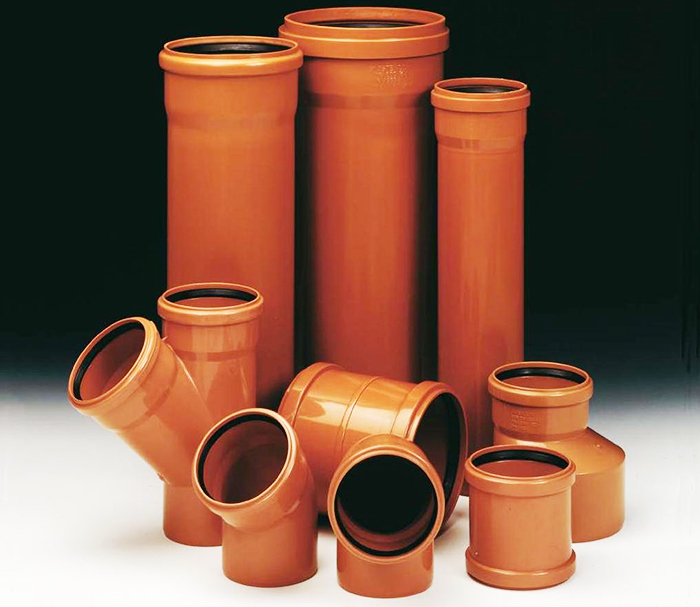
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
PVC pipes are used in gravity and pressure sewerage systems, both domestic and industrial. Depending on the accuracy class, they are marked as follows:
- SN2 - light, for shallow depth, do not cross the carriageway;
- SN4 - medium, can be laid under small roads for light vehicles;
- SN8 - heavy (fortified), can be used under highways and industrial roads.
PVC pipes for pressure sewerage are standardized by GOST R 51613 - 2000. They have 13 standard sizes with an inner diameter of 63 mm to 315 mm. For gravity sewer systems, a separate building standard VSN 48 - 96 is used. The range of standard sizes is rather limited: 50, 90, 110 mm with a length of 0.5 to 8 m and a wall thickness of 3.2 mm.
Benefits:
- strength with low weight;
- resistance to aggressive chemical and biological agents;
- smooth inner surface;
- ease of installation.
Disadvantages:
- rather narrow operating temperature range: -10 ° C ... + 40 ° C.

Asbestos-cement and concrete
Asbestos-cement concrete sewer pipes have a common area of use, as well as similar advantages and disadvantages. Most often they are used in outdoor gravity systems and in large highways. Manufactured in large diameters up to 1200 mm. Strength characteristics correspond to the following standards: concrete - GOST 6482-88, asbestos-cement - GOST 1839-80.
Advantages:
- corrosion resistance;
- high chemical resistance;
- resistance to static mechanical stress.
Disadvantages:
- heavy weight;
- fragility. Absolutely do not tolerate mechanical shock;
- asbestos-cement pipes have a negative impact on the environment.
Ceramic
Ceramic pipes, as a rule, are used to organize sewage systems in enterprises with aggressive drains containing chemically active elements. Technical parameters must comply with GOST 286–82. Diameter (up to 1200 mm) allows their use in highways with high-intensity wastewater traffic.
Benefits:
- complete immunity to almost any chemical attack;
- the large wall thickness allows the use of ceramic pipes without additional reinforcement under roads with heavy truck traffic.
Disadvantages:
- small length of one section and significant weight, which significantly increases the labor intensity and duration of installation work;
- low level of resistance to impact deformations. During installation work, you must be extremely careful;
- sensitivity to negative temperatures.When frozen, ceramics are destroyed. The installation depth must be observed or thermal insulation provided.
How to make the right choice of pipes for sewage by size and type
When choosing sewer pipes, they are guided, first of all, by the area of their use and the type of sewer system.
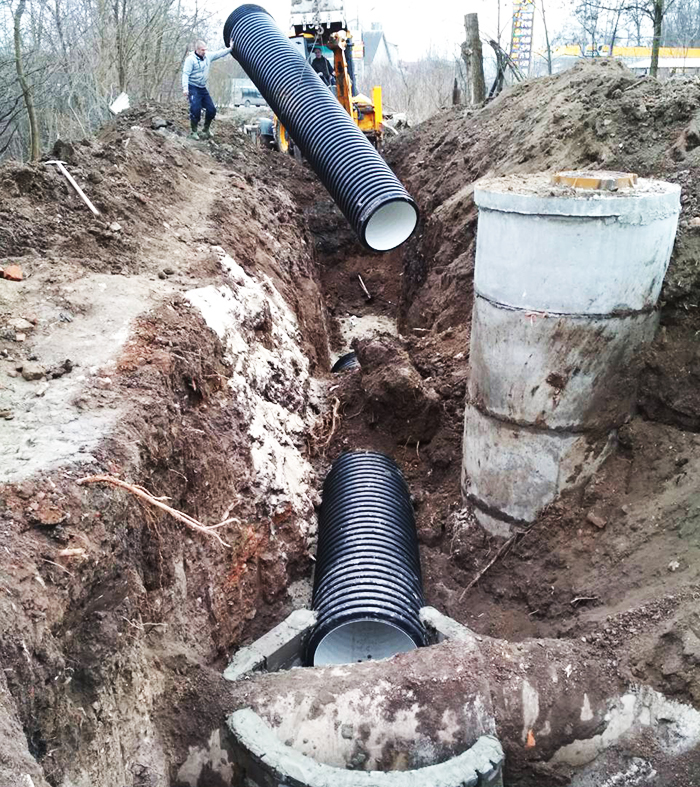
- Outdoor. The main requirements for external sewer pipes are a wide temperature range and resistance to external mechanical influences. If for domestic sewage it is allowed to use thin-walled and smooth polypropylene and polyethylene pipes, then concrete, ceramic and steel products with improved strength characteristics are used for main pipelines. It is also allowed to use two-layer corrugated polymer pipes for laying highways under roads with medium traffic.
- Internal. For residential, commercial and a number of industrial premises, there are general requirements for the sewage system described in GOST R 56534-2015. All these requirements are fully met by polymer pipes: PVC, polyethylene or polypropylene. Considering the wide range of standard sizes, low weight and ease of installation, at the moment other materials can hardly compete with them. Only a few chemical and food industries use ceramic and metal pipes for industrial sewage systems.

Plastic pipes are produced in the same standard sizes as cast iron and are quite compatible
PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
- Pressure. The pressurized sewerage system is usually used centrally for pumping wastewater to wastewater treatment plants. Its elements are subject to special requirements for the strength of not only the pipes themselves, but also their joints.
They are required to:
- versatility - the ability to transport various types of drains;
- resistance to water hammer;
- low susceptibility or complete inertness to chemical and biological corrosion;
- resistance to static pressure;
- manufacturability and high speed of installation, combined with the reliability of the joints.
All these criteria are met by PVC-U or HDPE pipes, although cement pipes are still quite common. The main parameter of a pressure sewer pipe is the maximum pressure of the working medium - MOP.
- Free-flow. Non-pressure sewer pipes do not impose such stringent operational requirements as for pressure pipes, in particular, for the parameter of annular stiffness. However, they must be sufficiently strong to withstand internal pressures up to 5 bar (4.93 bar). Their diameter should be selected in such a way that the filling rate does not exceed 80%.
Related article:
In the article, we will take a closer look at how do-it-yourself sewage scheme in a private house with step-by-step photos and videos, as well as learn how to choose the right pipes and fittings for its arrangement.
Diameter selection
The range of pipes used for the arrangement of domestic sewage systems is rather narrow and fits in the range of sizes from 40 mm to 220 mm. In accordance with the current building codes, as well as the recommendations of the manufacturers, the following diameters are used:
- 50 mm – shells, sinks (single and twin);
- 75 mm – shower trays, urinals, bathrooms;
- 110 mm – toilet bowls, central sewer risers, removal of the fan valve;
- 110-150 mm - wiring of a complex sewage system, performed in the basement;
- 160 mm - outlet from the central riser to an external septic tank.

Polymer pipes are distinguished by an especially wide range of standard sizes, which is associated with the manufacturability of their manufacture
PHOTO: ua.all.biz
Manufacturers
Special attention should be paid to the quality of pipe manufacturing. As a rule, all defects are immediately visible on the surface of the product, but sometimes the material of manufacture does not correspond to the declared specifications, which sharply reduces the duration of operation. It is recommended to use the products of the following manufacturers:
- Wavin (Netherlands)... Polymer pipes for domestic and outdoor gravity sewer systems. Two-layer corrugated pipes "Pragma" made of polypropylene are especially popular in the domestic market. Their tool joints have improved seals.
- Polyplastic (Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan)... Produces a wide range of pipes with a diameter of 40-600 mm from polyethylene, polypropylene, PAH, fiberglass. Particular attention should be paid to the Korsis series, which includes two-layer and reinforced pipes. These products have a characteristic appearance - an outer corrugated layer (black) and an inner smooth surface (yellow, orange, light blue).
- Ostendorf (Germany)... It has factories all over the world, including since 2011 in Russia. Manufactures pipes, fittings and fittings made of high strength polyvinyl chloride without impurities. The KG product line deserves special attention.
- Duker (Germany), Saint-Gobain (France). Pipes are produced from cast iron by centrifugal casting. Diameter 75-200 mm. The products of these companies are quite similar both in price range and in their performance characteristics.
Below are photo examples of the use of sewer pipes made of various materials
- PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
- PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
- PHOTO: stroyklim.com
- PHOTO: kanalizaciya-prosto.ru
- PHOTO: santechsystems-21.ru
- PHOTO: trubovar.ru
Non-standard use of sewer pipes.
- PHOTO: i.pinimg.com
- PHOTO: i.pinimg.com
- PHOTO: i.pinimg.com
- PHOTO: i.pinimg.com
You can additionally study the features of the choice of sewer pipes and their classification by reading the proposed video.