Which linoleum substrate is better: comparison of materials and scope
To improve the technical characteristics and extend the life of linoleum, many manufacturers and craftsmen recommend using special materials as an initial, rough layer. In this article, we will analyze which linoleum substrate is better, what functions it performs, when it is necessary, and when you can do without it. We will also provide a brief overview of popular manufacturers, consider their products and reviews on it.
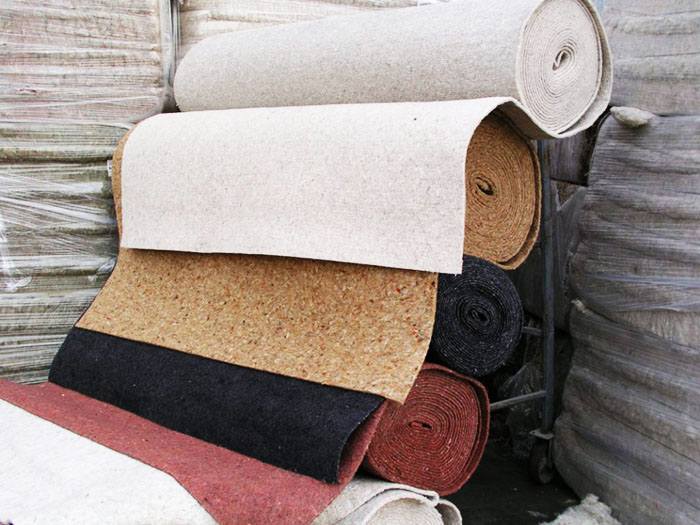

The building materials market offers many varieties of substrates, but not all of them can be used for laying linoleum
PHOTO: polonest.ru
The content of the article
Underlay functions
The linoleum underlay prevents the flooring from contacting the substrate. It performs the following functions:
- compensates for defects and minor unevenness of the base, which protects the flooring from premature wear;
- increases sound insulation. Especially useful in multi-storey residential buildings with reinforced concrete slabs;
- improves thermal insulation. Suitable substrates are recommended for use on the first floors of buildings located above unheated basements or when arranging floors on the ground.
Unlike laminate, linoleum is a soft floor material, therefore, the optimal thickness and rigidity of the substrate should be selected so that the surface of the floor covering does not deform under external influences.
The type of base must also be taken into account, in particular its effect on the interlayer material. Concrete floors and sand-cement screeds that have direct contact with the ground can absorb moisture, therefore, in addition to waterproofing, it is advisable to choose a moisture-resistant substrate.
Related article:
What linoleum to choose for home: types of flooring, sizes, markings, criteria for the correct choice by room, tips and tricks - in our article.
Technical parameters and performance characteristics by type
Thickness can vary between 2-10 mm:
- 2-5 mm is the optimal thickness for materials with average performance. Laying on a concrete base with minor defects is allowed, but it is better to fix them using a leveling fill;
- 2-3 mm - thickness of natural semi-rigid substrates (cork);
- 5-7 mm - the thickness of synthetic materials, which tend to compact by 25-40% during operational loads;
- 5-7 mm - fibrous and non-woven materials for rooms with additional sound and heat insulation;
- 10 mm and more - rigid self-supporting, performing the function of a subfloor.
Depending on the influence of the external environment and the characteristics of the operation of the room, additional properties may be required from the substrate:
- moisture resistance;
- antiseptic;
- ecological purity (hypoallergenic).
Jute
The jute fiber of which the backing is made is resistant to combustion, rot and mildew. It is an efficient, environmentally friendly insulation, which is realized both in mats and in rolls. Jute is widely used as the bottom layer of premium heterogeneous linoleum. Due to its rather high cost, this material is not widely used in Russia. Typically only used if there is no other alternative. When purchasing it, you need to pay attention to the density. Even when pressed firmly with your fingers, it should not deform. Thick and soft jute mats provide better thermal insulation, but as a result of prolonged use, the risk of dents on the flooring increases significantly.
Cork
The material consists of crushed cork wood, pressed with glue. Thickness from 1.5 to 4 mm in rolls and over 4 mm in mats. Has a lot of advantages:
- good sound insulation, especially from shock and vibration noise;
- low thermal conductivity;
- moisture resistance (does not rot);
- fugnicidal properties - resistance to mold and mildew.
Among the shortcomings, one can note the rather high cost of the material, the price of which is tied to fluctuations in the exchange rate, since all raw materials are imported.
There are several types of cork backing:
- ordinary (classic) - pressed cork chips;
- with rubber - synthetic rubber acts as a binder. The material is distinguished by a high degree of absorption of shock-vibrating sounds;
- with bitumen (parkolag) - has a two-layer structure, cork chips are glued to the building board with the help of a bituminous binder. In warm rooms, a specific smell of bitumen may appear.
Coniferous
The coniferous backing consists of shredded wood, wood fibers and pine needles, compressed with minimal or no adhesives. It is most often realized in the form of mats with a thickness of 3.6-7 mm. In rolls (option with glue) it comes across much less often, thickness 2-3.5 mm. The density of the material is 240 kg / m³. Has a low thermal conductivity - less than 0.050 W / (m ∙ K). It absorbs shock noises well. Provides an optimal level of shock absorption and significantly increases the durability of linoleum. The material is completely environmentally friendly. Mats with a thickness of more than 4.5 mm at the ends have a thorn-groove connection, which greatly facilitates installation and completely eliminates the formation of joining lines on the linoleum surface.
The substrate has an average resistance to mechanical stress, is quite sensitive to moisture, and can absorb odors. Another significant drawback is the rather high cost.
Linen
Linen backing consists of environmentally friendly material - linen fibers, bonded by mechanical pressing without the use of glue mixtures. It is sold in rolls with a thickness of 5-8 mm, density is 0.4-0.7 kg / m². Low thermal conductivity (up to 0.05 W / m³) allows it to be used for insulating the floors of the first floor. Additional benefits include the following:
- environmentally friendly - does not cause allergic reactions, does not have an unpleasant odor;
- effective - with a thickness of 6-7 mm, it is able to hide defects on the surface of the base up to 2.5-3 mm high.
- environmentally friendly - it is allowed to use commercial linoleum as additional insulation in schools and hospitals.
Felt
Non-woven polyester fabric with good insulating properties, especially the level of impact noise is reduced. Most felt substrates are impregnated with special non-toxic compounds that make the material less susceptible to decay and oxidation. During operation, the felt compaction and shrinkage are possible, and therefore dents can form on the surface of the flooring material in places of frequent use.
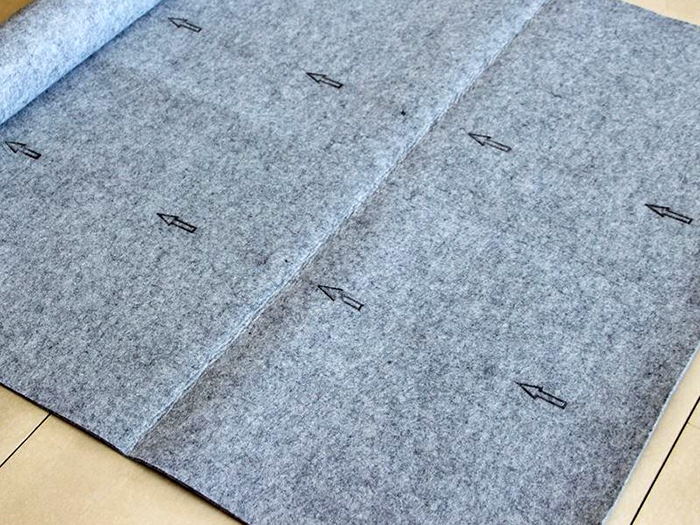

Roll felt has an optimal combination of technical characteristics and cost
PHOTO: russian.alibaba.com
Polymer materials
Polymeric materials - polyethylene or polypropylene - are used as synthetic linings for linoleum. They are sold under various trade marks, for example, penoizol, isolone, etc. Available in rolls. They differ in small thickness and rather mediocre technical characteristics. During operation, such a substrate cakes and pushes through, as a result of which characteristic waves are formed on the linoleum surface. Despite this, the material is quite popular due to its budgetary cost. Most home craftsmen and very many linoleum manufacturers strongly discourage the use of foamed polymer materials as a substrate.
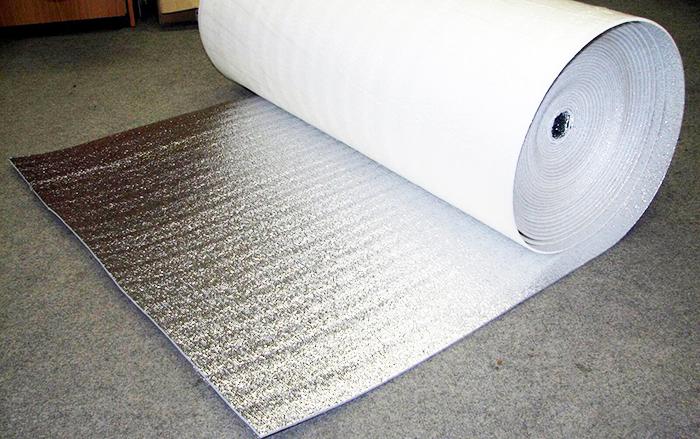
Foil
Consists of two layers: expanded polyethylene (polypropylene) and aluminum foil. More often used under laminate and warm floor... Aluminum gives the composite extra strength and reflects infrared radiation back into the room, making it an extremely effective thermal insulation material. It is laid with a reflective layer to the room.
Important! On concrete and cement-sand substrates, foil can react with cement alkalis.

The process of installing a foil substrate - it is shot with a construction stapler to a wooden base
PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
Combined
They are one of the most expensive, but the most effective. The composition can be completely natural, synthetic or blended, which uses jute, linen and synthetic fibers. Thickness up to 3 mm, roll length up to 10 m.It has a number of advantages over both synthetic and purely natural materials:
- high density and, as a result, excellent wear resistance and durability;
- hypoallergenic and minimal likelihood of mold and mildew;
- small coefficient of thermal conductivity - no more than 0.04 W / (m · K).
Related article:
How to choose glue for linoleum: advantages and disadvantages of use, classification of adhesive mixtures, their area of application, leading manufacturers and brands of glue, the sequence of actions for self-laying linoleum.
When you need a backing and when you can do without it
There is a list of factors, each of which leads to the need to use different types of substrates for linoleum:
- cold floor.A thick substrate, preferably made from natural materials, is a budget alternative to special insulation technologies: expanded clay screed, floating floor on extruded polystyrene foam, etc. It is used if the room is located above an unheated basement;
- use as a floor covering of single-layer linoleum. The use of this material without a backing will not only fail to provide the required heat and sound insulation, but can also reduce the load on the surface of the floor covering due to its shock-absorbing properties;
- correction of minor defects. The use of a substrate allows you to do without leveling fill, as it can hide irregularities from 1.5 to 3 mm.
Linoleum can be laid without an additional substrate in the following cases:
- multilayer linoleum is used, which already has a substrate of jute, expanded polystyrene or polyvinyl chloride. The price of such a coating differs slightly from the total cost of a single-layer linoleum and a separate substrate, but its use gives additional advantages. The laying process is greatly simplified and accelerated. The composite material itself is much stronger and more durable due to the presence of an additional fiberglass bonding layer;
- single-layer linoleum is laid on the old coating: linoleum, parquet, laminate. At the same time, the action of high mechanical loads is not allowed on the floor covering, and the surface of the base must be perfectly flat.
In what cases and which linoleum substrate is better
The choice of the optimal substrate material for linoleum depends on two main factors (not taking into account cost): the substrate material and the operational requirements. It should be noted that the subfloor material imposes only some restrictions, which can be easily circumvented by making, for example, a polymer-cement leveling fill.
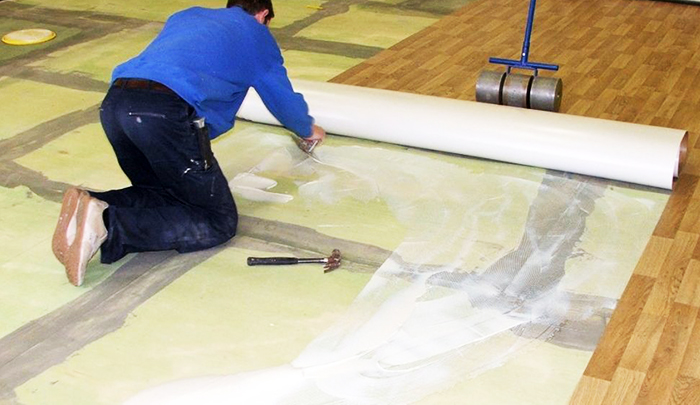

Laying linoleum on extruded polystyrene foam is allowed only in the case of careful sealing of the cracks
PHOTO: zamolotkom.ru
- For insulation. Fibrous and natural substrates have the best thermal conductivity indicators: jute, felt, linen and combined. However, they are all quite thick. An alternative solution is a cork substrate, characterized by a fairly high thermal resistance and low thickness.
- For waterproofing. Linoleum itself is a fairly good moisture-insulating material, but when using a multi-layer heterogeneous coating on concrete bases that have direct contact with the ground or are located above unheated basements, the lower layer must be additionally protected. For this, synthetic substrates made of foamed polymers, foil-clad polyethylene are used.
- For soundproofing. There are several types of noise:
- structural - occurs due to direct contact of various objects with the floor covering;
- acoustic - sound waves bouncing off the ceiling and walls;
- spatial - it is prompted by the combination of both previous factors.
Fiber and cork substrates with a thickness of 5 mm or more, as well as foam polymer coatings, are also used as soundproofing materials.

There are also special sound-absorbing materials, for example, weberfloor acoustic floor
PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
- For alignment. High-density substrates are used in the form of mats: combined, polymer (foamed polypropylene or polyurethane foam) or coniferous.
Related article:
How to lay linoleum with your own hands: preliminary preparation of bases of various types, features of measurement of premises, cutting, technology of laying in dry, using glue.
Leading manufacturers, their products and reviews
A short overview of the best linoleum substrates was compiled on the basis of aggregate information taken from Internet resources: vyborok.com, otzovik.com, irecommend.ru.
Table 1. Average cost of linoleum substrates
| Substrate type | Model / Manufacturer | Features and scope | Price as of October 2019, RUB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jute | EcoRoll / SoundGuard | For linoleum, laminate and parquet. A dense roll material, 3.5 mm thick, consisting of randomly intertwined jute and polyester fibers in a combination of 50 × 50 | 1700 (per roll 10 m²) |
| Jute | 20791 / Resource | For laminate, linoleum. Roll, natural jute, thickness 4 mm. Well compensates for unevenness of the base, antifungal impregnation. Has an unpleasant odor that disappears in a few weeks | 1300 (per roll 10 m²) |
| Foam-polyethylene | NPE-3 / Porileks | High pressure polyethylene. Biologically neutral, not susceptible to fungus and decay. Roll material, thickness 3 mm | 950 (per roll 52.2 m²) |
| Foam-propylene | 12331 / Isopak | Roll material for laminate, linoleum, parquet boards. Thickness 3 mm. High performance of thermal insulation and noise absorption | 1300 (per roll 52.5 m²) |
| Foam-propylene | 87408 / Professional | Roll material for laminate, linoleum, parquet boards. Thickness 3 mm. High performance of thermal insulation and noise absorption | 1100 (for 10 m²) |
| Foam-propylene | 2184 / Tuplex | Roll material for laminate, linoleum, parquet boards. Thickness 3 mm. High performance of thermal insulation and noise absorption | 3800 (for 33 m²) |
| Cork | BASIS / Cork | Environmentally friendly natural, hypoallergenic material. Resistant to mold and mildew. Sold in rolls, 2 mm thick | 1250 (for 10 m²) |
| Cork | 955 / MGO | Environmentally friendly natural, hypoallergenic material. Resistant to mold and mildew. Sold in rolls, 2 mm thick | 1480 (for 10 m²) |
| Cork | PPR05 / Corksribas | It is realized in slabs, thickness 5 mm. Levels bases well | 5800 (for 10 m2) |
| Coniferous | Unde-floor / STEICO | Available in mats 3, 4.5 and 5 mm thick. Composition: pine needles, wood fibers and paraffin. Has elasticity, resilience, absorbs vibration noise well, compensates for unevenness of the base | 1260 (7 m²) |
| Coniferous | lattialeijona-4.5 / LATTIALEIJONA | Available in mats 3, 4.5 and 5 mm thick. Composition: pine needles, wood fibers and paraffin. Has elasticity, resilience, absorbs vibration noise well, compensates for unevenness of the base | 840 (6 m²) |
| Coniferous | 95109 / Izoplaa | Available in mats 3, 4.5 and 5 mm thick. Composition: pine needles, wood fibers and paraffin. Has elasticity, resilience, absorbs vibration noise well, compensates for unevenness of the base | 1460 (9 m²) |
Review of the Isoplaat laminate underlay:
Feedback on the Profitex laminate underlay:
Feedback on the substrate for laminate sheet Grace:
Review of cork underlay for Albau laminate:
Summing up
The use of substrates for linoleum is not necessary in all cases, because many brands of this flooring material are already equipped with them. However, their use undoubtedly significantly improves the performance characteristics of the floor covering, in particular, heat and sound insulation.
If the article turned out to be useful to you, share the link with your friends and take part in its discussion.