Types of roof insulation - choosing the best material
The modern market for thermal insulation materials is overflowing with offers of a wide variety of insulation materials. In addition to the low coefficient of thermal conductivity, they can radically differ in their technical and operational characteristics. At the same time, the roof of a structure, depending on the design and operating conditions, makes special demands on the parameters of the used thermal insulation. This article will describe the main characteristics of common thermal insulation materials, analyze and compare them. We will tell you how to choose a roof insulation depending on the type of its construction: flat, pitched, attic, and provide information about the best manufacturers and real reviews of their products.

Up to 30% of all heat losses of the building occur through the roof, therefore, its thermal insulation must be given the utmost attention.
PHOTO: gerchuluuconstruction.com
The content of the article
General requirements for thermal insulation for the roof
The selection of the optimal insulation for the roof is carried out according to a number of criteria.
- Coefficient of thermal conductivity. For most modern thermal insulation materials, this figure is below 0.04 W / m · K. This is quite enough to use a small layer of thermal insulation, even in the harsh domestic climate.
- Density. The indicator is inversely proportional to the coefficient of thermal conductivity. The density of the heat-insulating material depends on how close to building structures it can be located. The absence of cracks prevents the appearance of cold bridges, the formation of condensation, deterioration of insulation and building structures.
- Weight. Quite a wide range of indicators from 15 to 300 kg / m². When insulating a wooden or prefabricated panel house with a pitched and mansard roof, it is recommended to use lightweight materials so as not to have a critical effect on the supporting structures.Stronger structures made of solid bricks, reinforced concrete monolithic and prefabricated structures can withstand significant loads. A heavier insulation is used for them.
- Moisture absorption. The absorption of condensed or atmospheric moisture by the insulation reduces its thermal insulation parameters. For such materials, it is necessary to provide for a waterproofing system and evacuation of fumes.
- Water vapor permeability. The complete absence of vapor permeability can lead to stagnation of warm humid air and the formation of mold. High vapor permeability will reduce the resistance to cold air masses and require additional wind insulation.
- Flammability. For timber structures, it is better to choose non-combustible thermal insulation materials. However, even brick and concrete buildings have pitched roofs, in most cases made of wood. For flat roofs made of concrete slabs, the use of combustible insulation is quite acceptable.
- Shrinkage and the ability to maintain its original shape. Due to the deformation of the material during operation, voids, cracks can form, and on steep pitched roofs - distortions that reduce the effectiveness of thermal insulation.
- Soundproofing. A key parameter, especially on "noisy" roofing materials: metal profiles, metal tiles, etc. Reduces the background sound during rain and hail.
- Ease of installation. An important parameter that allows you to perform part or all of the roof insulation work yourself. In addition, important qualities are: the need to use specialized equipment, as well as the formation of residues that cannot be used.
Types of roof insulation
Conditionally, all heaters can be divided into natural and synthetic. Their environmental friendliness and efficiency largely depend on this parameter. In the review, we will not touch upon exotic thermal insulation made from reeds, reed or straw mats.
Glass wool
It has a fibrous structure; inorganic raw materials are used for the manufacture, also used in the production of glass. Glass wool is resistant to mold, mildew and rot. One of the few heaters in which rodents do not start. It has high heat and sound insulation parameters, combined with an affordable cost. Among the shortcomings, one can note the need to use personal protective equipment during installation, as well as the need for thorough isolation from living quarters - as a rule, a vapor barrier film is used for this. Thermal conductivity - 0.035-0.044 W / mK.
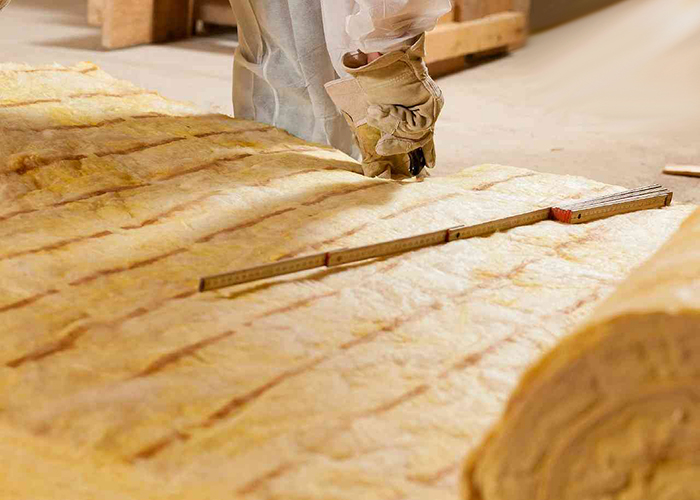

When installing glass wool, it is imperative to use personal protective equipment: tight overalls, gloves, glasses, respirator
PHOTO: lh3.googleusercontent.com
Minvata, basalt wool
Basalt (stone) wool is actually a mineral wool, but with improved manufacturing technology and better raw materials from volcanic rocks (basalt, diabase). It is more resistant to mechanical stress. The material is more durable than glass wool. It is produced both in rolls and in slabs. The recommended density for insulating unloaded roof structures varies from 30 kg / m³ to 40 kg / m³. For loaded but unused flat roofs, it is better to use denser grades of 45-60 kg / m³. With appropriate reinforcement and waterproofing, they can withstand technical movements and standard snow loads. Thermal conductivity - 0.032-0.048 W / m K

Mineral and basalt wool for a layman is visually difficult to distinguish from each other. When purchasing, require a certificate of conformity
PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
Important! The service life of mineral wool, according to manufacturers, is 25-30 years. Basalt is slightly more - up to 35 years old. However, in harsh climatic conditions, it is much less and for roof structures it really is no more than 20 years. After that, the effectiveness of thermal insulation begins to decline sharply.
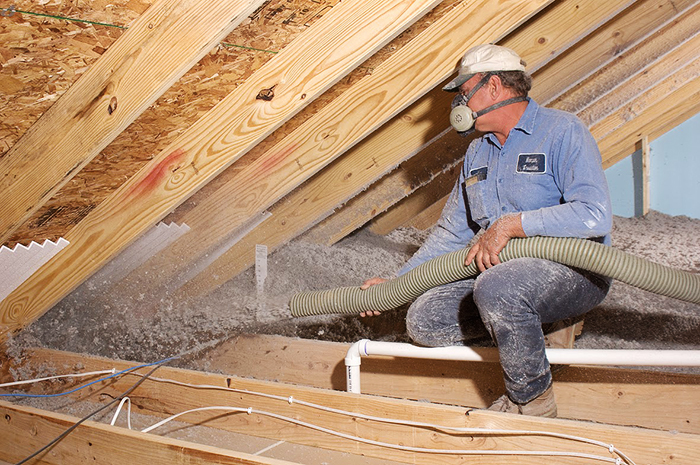
Ecowool
The material consists of specially treated cellulose, as a rule, this is recycled paper, an adhesive mixture with antiseptic and flame retardants in a ratio of 81% to 19%. Externally, the insulation is a loose mass of dry flakes. Manufacturers position the material as a universal, and most importantly, environmentally friendly means for insulating all building structures at home.
It is used for insulating attics and backfilling attic floors - horizontal unloaded surfaces (between logs), operated attics. Blowing technology is used to insulate roof structures. With the help of special equipment, ecowool is blown into the space, between the rafters or logs.

Styrofoam
Two types of foam can be used to insulate attic structures and roofs:
- For pitched - ordinary expanded polystyrene PPS-25 ... PPS-35;
- For flat - extruded foam (penoplex), with a density from 32 kg / m³ to 45 kg / m³.
The thermal conductivity of the entire class of insulation based on expanded polystyrene is 0.38-0.41 W / mK. The advantages of this material include:
- durability, while the performance properties are not lost throughout the entire service life;
- resistance to mold, mildew, decay, corrosive processes;
- complete hydrophobicity - does not get wet and practically does not absorb moisture;
- light weight - no need to strengthen the supporting structures;
- the possibility of cutting with a simple knife, the small elasticity of the material allows for quick installation;
- good sound insulation characteristics;
- affordable cost - one of the cheapest thermal insulation materials.
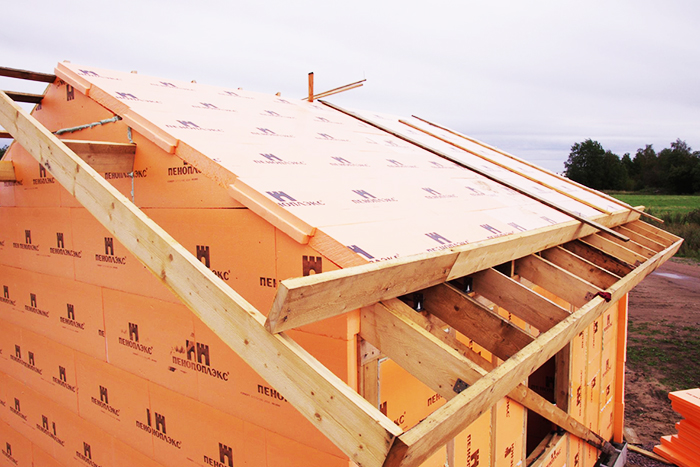

It is usually used for insulating roof structures in surface-mounted technologies, when all layers of the roofing cake are mounted outside the building.
PHOTO: teplo.guru
Disadvantages of expanded polystyrene and insulation based on it:
- release of carcinogenic substances. Depending on the characteristics of the production process, they may exceed the norm, therefore, upon purchase, it is necessary to require the appropriate certificate from the seller;
- high flammability in combination with the active release of toxic substances during combustion;
- complete tightness - insulated structures become vapor-tight, therefore, attic and attic rooms insulated with foam plastic require a forced ventilation system.
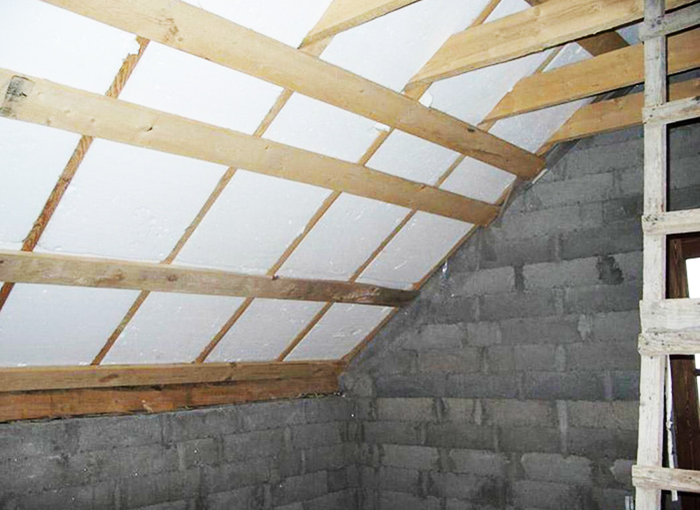

When using foam as insulation, there is no need for additional vapor barrier
PHOTO: utepleniedoma.com
Related article:
Penoplex: technical characteristics. Having picked up slabs of suitable thickness, you can ensure a sufficient level of thermal insulation of the walls, floor, ceiling. Let's talk about this insulation in more detail in our review.
Penofol, penotherm
This heat-insulating material is a composite based on low-pressure polyethylene foam and one (penofol) or two (penotherm) foil layers. The thermal conductivity of such heaters, in comparison with thick-layer materials, is not so high and amounts to 0.049 - 0.053 W / m · K. However, the effect of insulation in attic rooms appears due to the reflection of infrared radiation into the room. For this, the insulation is mounted with the reflective side to the living space. And between it and the inner surface of the rough coating, a technological gap of 3-5 cm is formed.
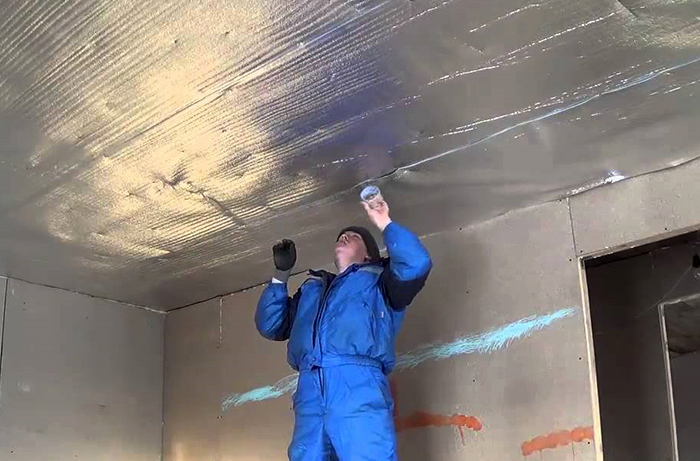

When laying penofol or penotherm, all joints between the canvases are sealed with a special metallized tape
PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
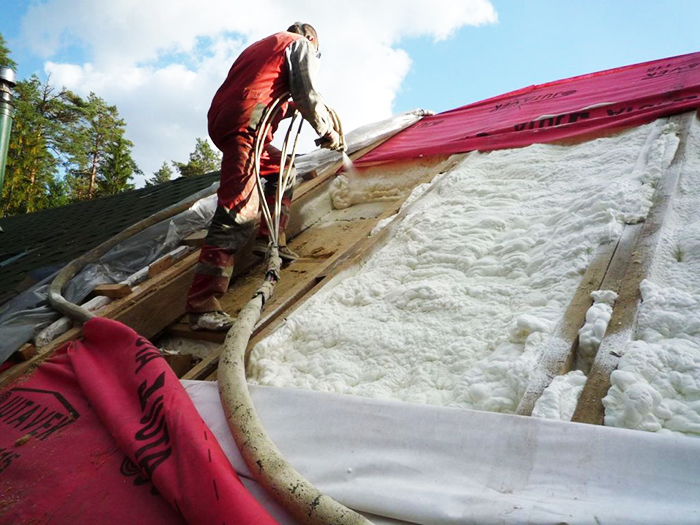
Polyurethane foam
The use of polyurethane foam as a heater for attic and roof structures involves the use of a spraying method.Thanks to this method, a seamless layer is created that does not require compaction, sealing of cracks and cross-laying of plates. Has the following parameters:
- thermal conductivity coefficient 0.029 - 0.041 W / m · K;
- density 70 kg / m³;
- durability up to 30-35 years without reducing the basic qualities.
For spraying polyurethane foam, it is necessary to have special expensive equipment, thanks to which the insulation of roof structures is carried out in a few hours. In addition, the cost of the insulation itself is much higher than that of conventional foam.

Spraying can be carried out on the base of the roof without additional waterproofing and wind insulation
PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
Important! By analogy with polyurethane foam, the technology of spraying mineral wool - "cotton blanket" (blowing) was developed. This method has all the advantages of polyurethane foam spraying, but is environmentally friendly.
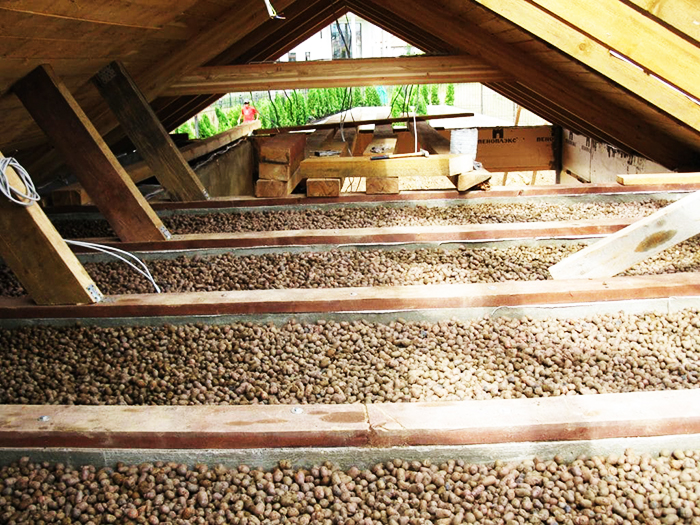
Expanded clay
Environmentally friendly heat-insulating materials are small balls of fired clay. Has an extremely low moisture absorption, non-flammable, vapor permeable. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of expanded clay, depending on the fraction, is 0.1 - 0.18 W / m · K, with a density of 250 to 800 kg / m³. As can be seen from these indicators, expanded clay has rather mediocre thermal insulation parameters. Therefore, to obtain the desired effect of insulation, it must be used with a thicker layer. Typically used as a filler for cement screeds on horizontal roof surfaces.
Sawdust
By its effect, as well as by the composition of thermal insulation, roof insulation with sawdust almost completely repeats ecowool. However, if ecowool is treated with boron to obtain resistance to decay and combustion, then it is not recommended to process sawdust. In this regard, such a heater requires particularly careful hydro and vapor barrier. Sawdust is susceptible to rotting and fungal attack, so the attic must be well ventilated.
As a rule, sawdust is laid on horizontal surfaces in a structure between logs or on pitched roofs with a small angle of rise. At the same time, the shrinkage factor of the material is minimal. Another undoubted advantage is the availability of insulation. As a rule, it is used by those who produce them as a result of various woodworking processes.
Comparison of the main technical and operational characteristics
To facilitate the selection process, all the main parameters of thermal insulation materials that can be used for roof insulation are summarized in one table:
Table 1. Main parameters of thermal insulation materials
| Options | Glass wool | Mineral / basalt wool | Ecowool | Penofol / penotherm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity, W / mK | 0,035-0,044 | 0,032-0,048 | 0.032-0.041 | 0,049-0,053 |
| Moisture absorption | Average | Average | Average | No |
| Flammability | No | No | Weak | High |
| Density, kg / m³ | 35-50 | 25-60 | 35-75 | 35-40 |
| Water vapor permeability, mg / (m h Pa | 0,50-0,54 | 0,32-0,37 | 0,30-0,67 | No |
| Shrinkage | Weak | Weak | Average | No |
| Sustainability | Low | Average | Average | Low |
| Ease of installation | Simply | Simply | Special equipment | Average |
Continuation of table 1.
| Options | Polystyrene foam / extruded foam | Polyurethane foam | Expanded clay | Sawdust |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity, W / mK | 0,38-0,41 | 0,029-0,041 | 0,1-0,18 | 0,065-0,095 |
| Moisture absorption | No | No | Very low | High |
| Flammability | High | Weak | No | High |
| Density, kg / m³ | 25-65 | 70-75 | 250-600 | 120-200 |
| Water vapor permeability, mg / (m h Pa | No | No | 0,23-0,26 | 0,26 |
| Shrinkage | No | No | No | Weak |
| Sustainability | Low | Low | High | High |
| Ease of installation | Average | Special equipment | Embankment | Embankment |
Leading manufacturers
- Rockwool. The corporate headquarters is registered in Denmark.Production centers in many countries of the world, including Russia. The products are distinguished by high quality at a reasonable cost. Produces mainly mineral and basalt wool in a wide range.
- Knauf. German company with production facilities in Eastern and Western Europe. Offers a wide range of construction products, including thermal insulation. In the production of mineral wool, phenol-formaldehyde resins are not used.

Knauf's product range includes mineral wool and basalt wool used for thermal and acoustic insulation
PHOTO: fb.ru
- TechnoNIKOL. Domestic manufacturer of basalt and mineral wool for insulation and sound insulation. The most popular line of high density mineral wool boards.

The assortment of products of the Technonikol company includes both mineral wool and insulation based on expanded polystyrene
PHOTO: tn.ru
- Isover. Subsidiary of the Saint-gobain concern. It is engaged in the production of a wide range of basalt and glass wool. The assortment includes roll and plate insulation, as well as shells for thermal insulation of pipes.
- Ursa. Rolled glass wool based insulation. Acrylic is used as a binder to prevent excessive fragility of the fibers. The structure of the insulation is rigid with high elasticity.
Choosing the type of insulation for the roof
The priority in the requirements for insulation is set by the customer himself or the contractor company based on the following data:
- roof parameters, which include the steepness of the slope, the complexity of the structure, the area, the thickness of the rafter legs and the material of their manufacture, the type of roofing material;
- passage through the roof of building structures and utilities;
- climatic conditions: amount and type of precipitation, average annual and peak negative temperatures;
- features of delivery, storage and installation;
- environmental friendliness;
- financial opportunities.
The photo below shows the types of thermal insulation materials for pitched and flat roofs.
- PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
- PHOTO: welltonpro.com.ua
- PHOTO: i.ytimg.com
- PHOTO: penopoliuretan.in.ua
- PHOTO: plusteplo.ru
- PHOTO: teplo.guru
Consumer reviews
Feedback on Linerock "Light effect" insulation:
Review of ISOROC mineral wool thermal insulation:
Another review of ISOROC mineral wool thermal insulation:
Review of Penoplex insulation boards:
Penoplex platesReview of ISOROC mineral wool thermal insulation:Penoplex plates
Summing up
Experienced builders recommend using slab and roll thermal insulation based on basalt wool for roof insulation. Subject to the observance of the technology of hydro and vapor barrier, it is able to serve for at least 30 years without reducing its basic performance. The use of foam increases the level of fire hazard of the structure. And the so-called "ecological" heaters are unreasonably expensive and not very effective.
If you liked the article, you learned useful information from it, share your opinion with us and recommend our site to your friends.