Vapor barrier for the walls of a wooden house: types and installation technology
In SP 31-105 (design, construction of energy-efficient frame dwellings), SP 64.13330 (wooden structures), the internal vapor barrier for the walls of a wooden house is specified without fail. This protective layer prevents the penetration of humid air into wooden structures, wadded insulation... External vapor barrier becomes necessary for external insulation, or for the operation of cottages in hot regions.
The content of the article
Video: what is hydro and vapor barrier used for
Purpose, types, characteristics
There are several types of insulation materials that individual developers usually confuse:
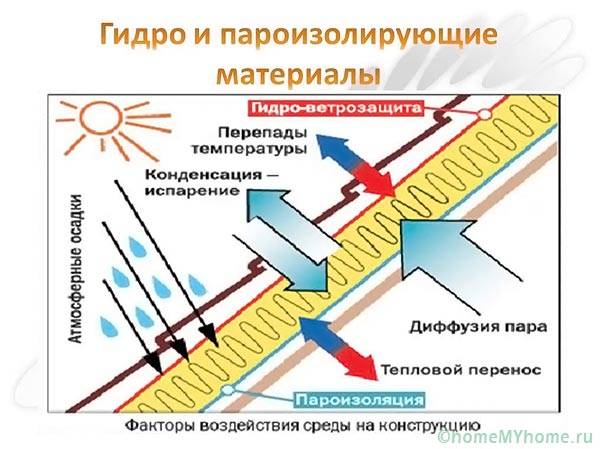
- waterproofing - cuts off only water, but lets in moist air;
- vapor barrier - retains moist air, preventing it from penetrating to the structural frame of the building, and, no matter what materials the building is built from;
- hydro-wind protection - used only in ventilated facade systems, roof pies, covers external thermal insulation, prevents the destruction of expanded polystyrene, mineral, glass wool from weathering.
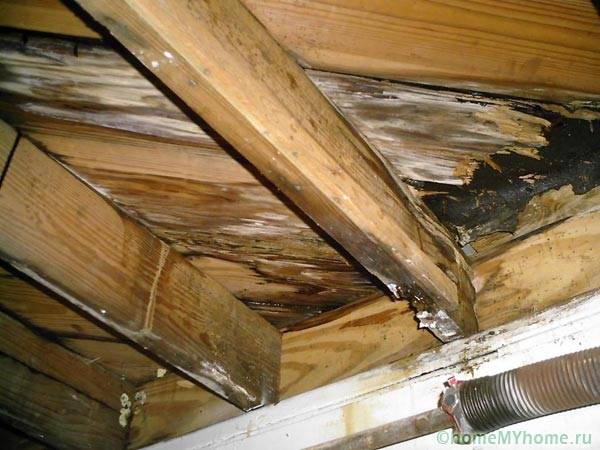
Vapor barrier for the walls of a wooden house is vital, since it reduces the operating budget of the cottage, increases the building resource. With a change in moisture content, lumber loses its geometry stability, is exposed to rotting, destruction.
The following structures are usually called wooden houses:
- log cabins - crowns of sanded or calibrated logs, planed or glued beams;
- "Skeletons" – timber frame sheathed with boards, OSB plates, drywall from the inside;
- half-timbered houses - a wooden frame, any filler can be used between the posts, including panoramic glazing;
- SIP panels - expanded polystyrene or polyurethane foam between OSB boards.
Therefore, for each construction technology, various vapor barrier materials are used - films, membranes, polymer varnishes. For example, of all the above structures, only log cabins made of cylindrical construction do not have external finishing. Therefore, the crowns on the outside are often coated with polymer varnishes.
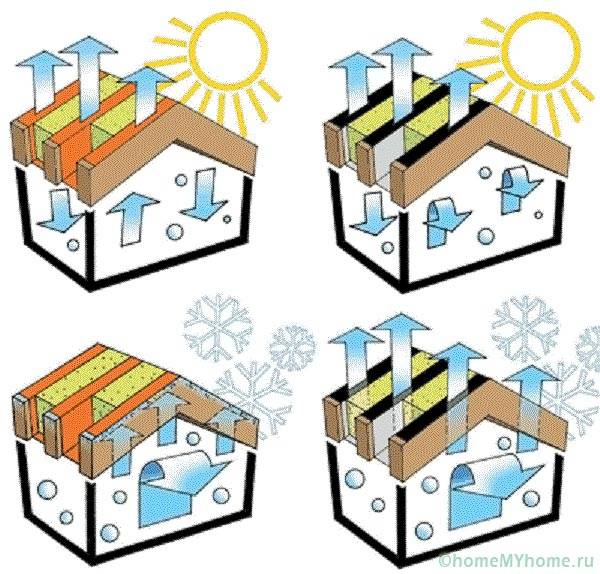
On frame, panel board, panel houses, the vapor barrier can be installed both outside and inside:
- if the dwelling is operated in a cold region, an internal vapor barrier is sufficient, which will cut off moist air from the premises;
- in hot climates in summer, the outside air is often much warmer than indoors, therefore, an external vapor barrier is additionally installed;
- if the cottage is insulated from the outside with mineral wool, expanded polystyrene through the ventilation facade system, moisture is removed due to air circulation in the ventilated space, however, hydro-wind protection is required insulation outside.
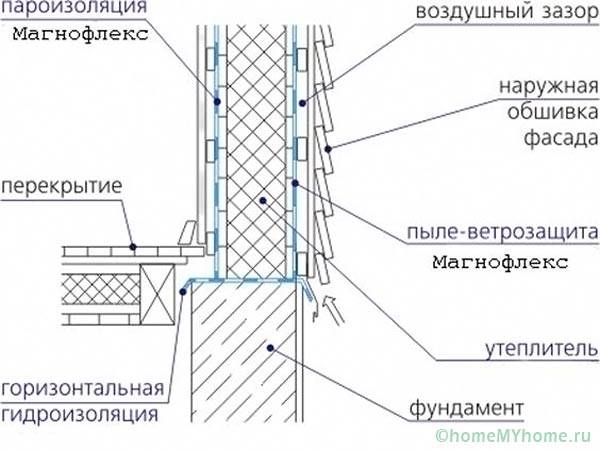
When installing a vapor barrier layer, consider:
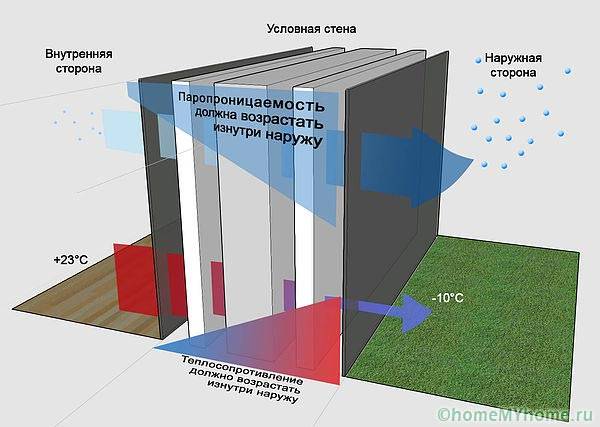
- some interior finishes have their own vapor barrier, so the layers in the building wall cake should be positioned in such a way that the vapor barrier properties increase from the inside out, otherwise the dew point will shift to the inside of the wall, condensation will form on the surfaces of the lumber;
- any vapor barrier material automatically makes the walls non-breathable, so mounting may be required forced ventilation (supply valves on the windows, fans in the walls, vents).
Related article:
Why do plastic windows in the house sweat? From this publication you will learn about all the reasons for this unpleasant phenomenon and how to get rid of it.
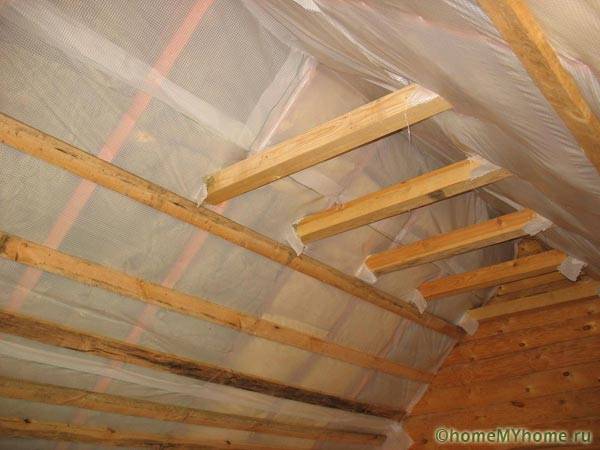
The main installation errors are the incorrect placement of the vapor barrier inside the cake of the walls, the inverted sides of the membrane, or the lack of continuity of the contours. Films on the walls should be joined with materials on ceilings and floors.
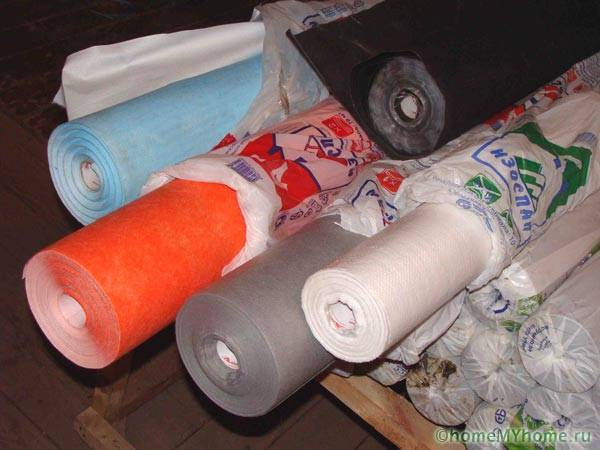
Films
The industry produces smooth polymer films without perforation, with maximum vapor barrier. For baths, saunaswith specific operating conditions (rapid heating to extreme temperatures), aluminum foil is glued to one or both sides. It reflects heat back, thus saving energy.
The most popular are polyethylene, PVC films, which are mounted either under the wall cladding or over the outer insulation. If, in violation of the standards of the joint venture, there is no internal vapor barrier of the dwelling, the film is installed outside under the basalt wool.
Membranes
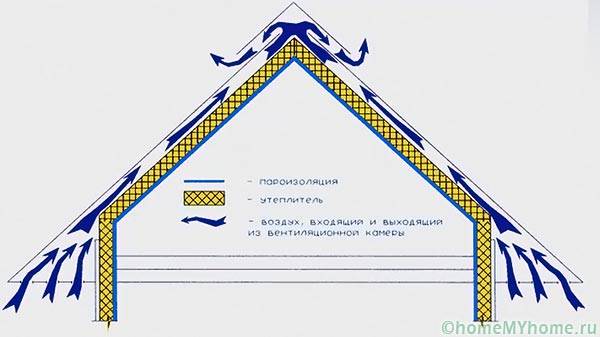
Diffusion membranes, in contrast to classic films, have a different design. The molecules inside them are arranged in a labyrinthine order, which makes it possible to condense moisture from the air on their surface, not to let it pass to the sawn timber from which the frame is assembled.
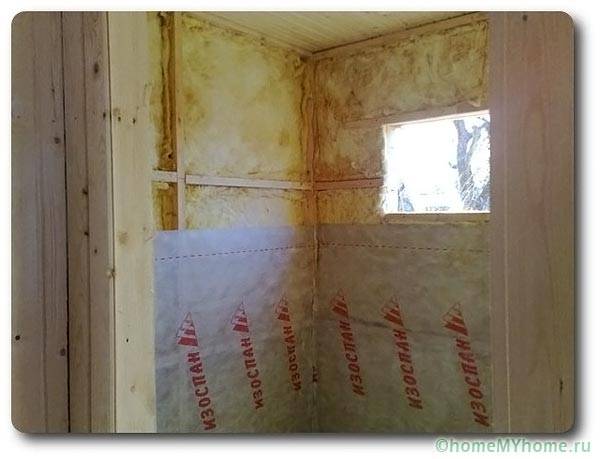
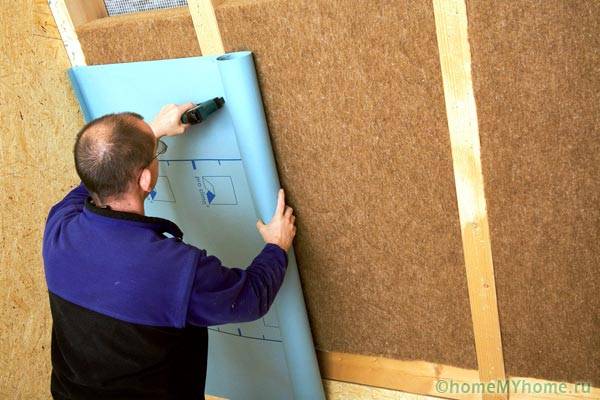
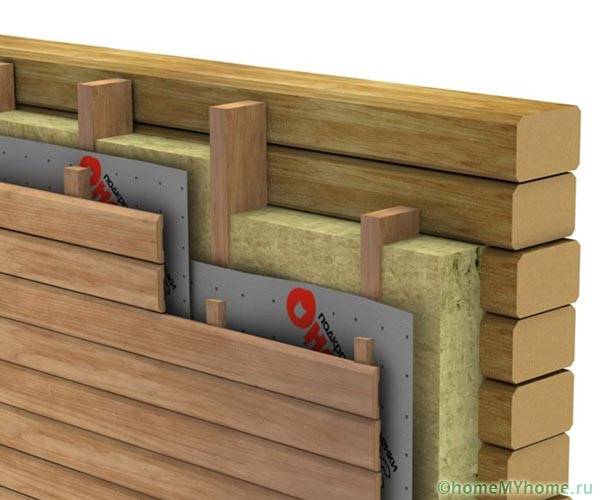
At the same time, it is necessary to install a vapor barrier for the walls of a wooden house using the following technology:
- under the inner wall cladding;
- with a mandatory ventilation gap between the decor and the film.
With an increase in moisture from the outside, vapors penetrate into the walls, but they can freely pass through the pores of the film, condensing on its inner surface. Thus, if you change sides during installation, the effect of the vapor barrier layer will be exactly the opposite:
- all moist air will pass into the wall;
- condensation forms on wooden structures.
Manufacturers mark each side of the membrane, provide products with detailed instructions that must be followed during installation.
Roll materials
Individual developers should not confuse roll materials with film materials. The last category is listed above, the following products belong to the roll-on vapor barrier:
- roofing felt - based on fiberglass or fiberglass with one layer of bituminous material;
- roofing felt - tar-soaked cardboard;
- glassine - cardboard impregnated with bitumen.
Attention! The vapor permeability of these materials is 50 times higher than that of polymer films and membranes, therefore their use in wooden housing construction is not recommended.
Polymer varnishes
Most often, varnishes with the VD-AAK-001D index are used to protect the decorative layer of log cabins. The material is ready to use, applied in several layers, retains the texture of wood, forms a protective film. Semi-matt, glossy, colorless varnishes are usually used, drying in 4-7 hours. The average consumption is 1 liter per 8 - 14 squares of surface.
If it is planned to decorate the interior walls with decorative materials in a log house, cheaper polymer films are used instead of varnish.
Selection criteria, installation technology
When designing a vapor barrier, the construction budget remains the main selection criterion. Therefore, in 90% of cases, polymer films with a thickness of 0.15 mm or more are used. Since they are covered with a decorative layer, the resistance to solar ultraviolet radiation can be ignored. However, there are nuances of choice:
- vapor barrier of walls from the inside of a wooden house is usually done with a budget plastic wrap;
- the vapor barrier of the walls of a wooden house from the outside is provided with a polypropylene or PVC cloth, since these materials are weather-resistant.
Membranes are used less frequently because they are heavier and more difficult to fix on vertical surfaces. Only walls of log cabins with a sufficiently attractive design are treated with varnishes, since this material is at least three times more expensive than others.
Films are shot with staples using a stapler, varnishes are applied with a brush, roller or sprayed with a special tool.
Pros and cons of vapor barrier materials
When choosing a vapor barrier, it is necessary to take into account the structural and operational characteristics of existing materials:
- diffusion membrane - only three-layer materials possess the required properties, which are expensive, the membrane can be mounted from the inside / outside without restrictions;
- polypropylene film - in 50% of cases, they cover unfinished objects for winter conservation, there are modifications with an absorbent layer for collecting condensate;
- plastic film - the only drawback is destruction from ultraviolet radiation, so it is necessary to cover the material from sunlight.
For the above reasons, polymer varnishes are used for a limited number of construction and finishing technologies.
conclusions
Thus, the home craftsman is able to independently choose a vapor barrier material, mount it to protect the wooden walls of the home. The most commonly used polymer films and membranes.
Video: insulation and vapor barrier of a frame house